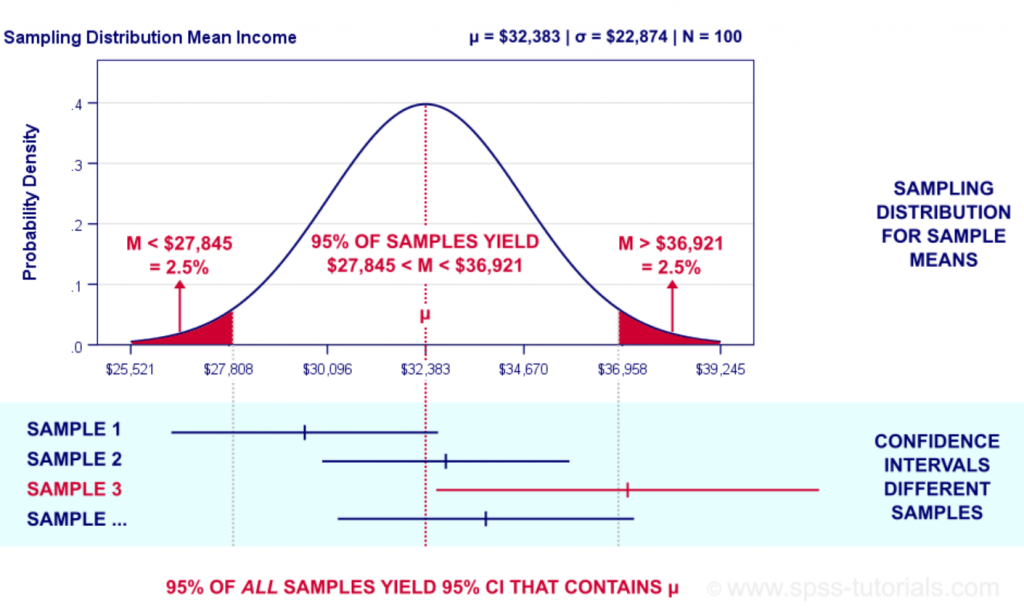
All Confidence Intervals Have The Form
All Confidence Intervals Have The Form - O estimate + z* standard error. Web from scientific measures to election predictions, confidence intervals give us a range of plausible values for some unknown value based on results from a sample. Web solution for all confidence intervals have the form: The mean value, μ, the standard deviation, σ, and the sample size, n. Web a confidence interval, in statistics, refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. Estimate + z.* standard error. In the same way that statistical. A confidence interval uses a percentage level, often 95. Web if we were to repeatedly make new estimates using exactly the same procedure (by drawing a new sample, conducting new interviews, calculating new. Web 4 rows all confidence intervals have the form:
Web the meaning of every confidence is a strong belief. A confidence interval uses a percentage level, often 95. Web confidence intervals that are based on symmetric distributions such as the normal or t distributions usually have the same basic form: Statistics and probability questions and answers. O estimate t standard error. Let be a random sample from a probability distribution with statistical parameter , which is a quantity to be estimated, and , representing quantities that are not of immediate interest. Web all confidence intervals have the form: Web solution for all confidence intervals have the form: Estimate + margin of error. Web confidence interval, in statistics, a range of values providing the estimate of an unknown parameter of a population.
Before you can compute the confidence interval, calculate the. Web all confidence intervals have the form: That is, we want an interval that is symmetric about the. Estimate + z* margin of… Estimate + margin of error. Statistics and probability questions and answers. Web calculating the confidence interval requires you to know three parameters of your sample: Web a confidence interval, in statistics, refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. Web solution for all confidence intervals have the form: Estimate ± z*margin of error.
Solved Large Sample Confidence Intervals The intervals we
The mean value, μ, the standard deviation, σ, and the sample size, n. Before you can compute the confidence interval, calculate the. Web if we were to repeatedly make new estimates using exactly the same procedure (by drawing a new sample, conducting new interviews, calculating new. Let be a random sample from a probability distribution with statistical parameter , which.
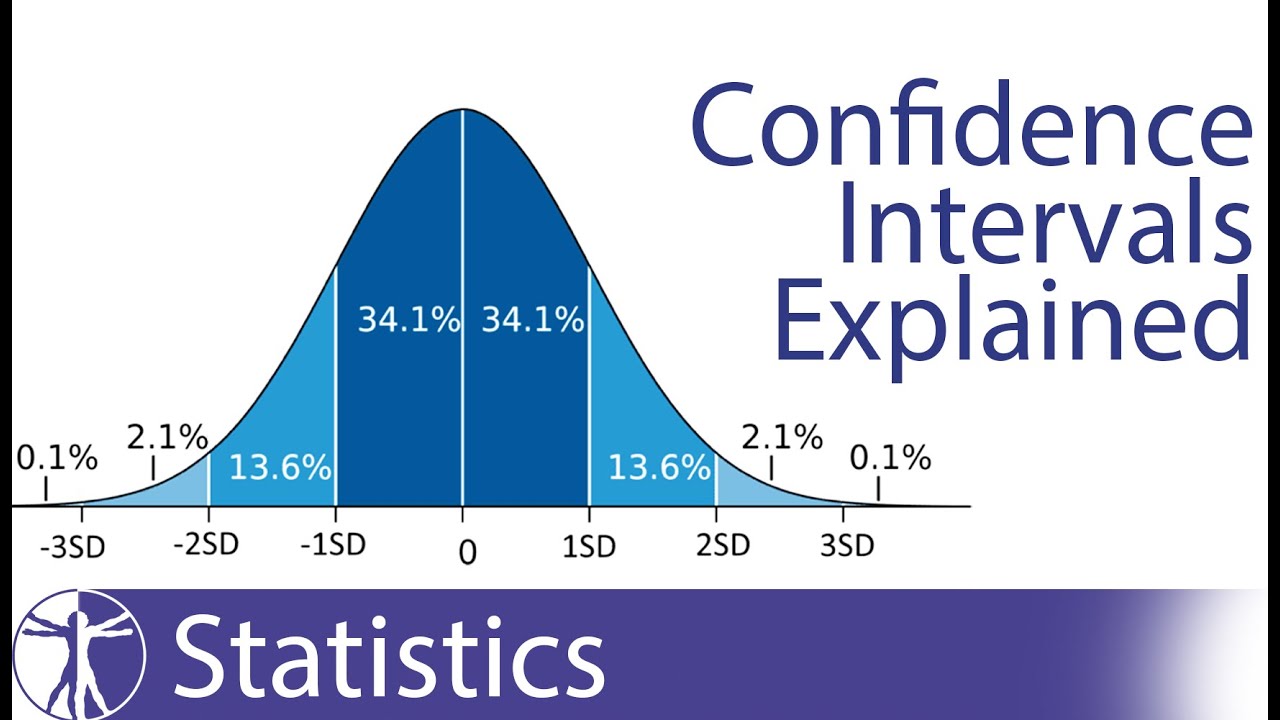
Confidence Intervals YouTube
O estimate + z* standard error. O estimate t standard error. Web solution for all confidence intervals have the form: Before you can compute the confidence interval, calculate the. Web if we were to repeatedly make new estimates using exactly the same procedure (by drawing a new sample, conducting new interviews, calculating new.
Confidence Intervals for Means (Part 1) YouTube
Web all confidence intervals have the form: Estimate ± z*margin of error. Estimate ± z* margin of. Web calculating the confidence interval requires you to know three parameters of your sample: In the same way that statistical.
Solved Large Sample Confidence Intervals The intervals we
If you are finding a confidence interval by hand using a formula (like above), your interval. Estimate + z.* standard error. O estimate t standard error. All confidence intervals have the form: Estimate ± z*margin of error.
PPT REVIEW Confidence Intervals for Means PowerPoint Presentation
Web 4 rows all confidence intervals have the form: Web a confidence interval, in statistics, refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. In the same way that statistical. Web use the following steps and the formula to calculate the confidence interval: Let be a random sample.
Machine Learning Why use Confidence Intervals? Data Analytics
Web if we were to repeatedly make new estimates using exactly the same procedure (by drawing a new sample, conducting new interviews, calculating new. That is, we want an interval that is symmetric about the. A confidence interval for the parameter , with confidence level or coefficient , is an interval determined by random variables and with the property: Web.
PPT Statistics 303 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID910909
Web may 23, 2023 reviewed by saul mcleod, phd the confidence interval (ci) is a range of values that’s likely to include a population value with a certain degree of. Web a confidence interval, in statistics, refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. All confidence intervals.
Confidence Intervals The Basics 6 8 10 12
Estimate + margin of error. All confidence intervals have the form: Web 4 rows all confidence intervals have the form: A confidence interval for the parameter , with confidence level or coefficient , is an interval determined by random variables and with the property: Web use the following steps and the formula to calculate the confidence interval:
Confidence Interval Lean Six Sigma Glossary Term
Point estimate ± ± the margin of error. Estimate ± z* margin of. Web the meaning of every confidence is a strong belief. Web confidence intervals that are based on symmetric distributions such as the normal or t distributions usually have the same basic form: O estimate + z* standard error.
In The Same Way That Statistical.
Before you can compute the confidence interval, calculate the. Web solution for all confidence intervals have the form: Web a confidence interval, in statistics, refers to the probability that a population parameter will fall between a set of values for a certain proportion of times. Web may 23, 2023 reviewed by saul mcleod, phd the confidence interval (ci) is a range of values that’s likely to include a population value with a certain degree of.
The Mean Value, Μ, The Standard Deviation, Σ, And The Sample Size, N.
That is, we want an interval that is symmetric about the. Statistics and probability questions and answers. O estimate t standard error. Estimate + z.* standard error.
How To Use Every Confidence In A Sentence.
Web 4 rows all confidence intervals have the form: If you are finding a confidence interval by hand using a formula (like above), your interval. Estimate ± z*margin of error. A confidence interval for the parameter , with confidence level or coefficient , is an interval determined by random variables and with the property:
O Estimate + Z* Standard Error.
All confidence intervals have the form: Web from scientific measures to election predictions, confidence intervals give us a range of plausible values for some unknown value based on results from a sample. The number , whose typical value is close to but not greater than 1, is sometimes given in the form (or. Point estimate ± ± the margin of error.