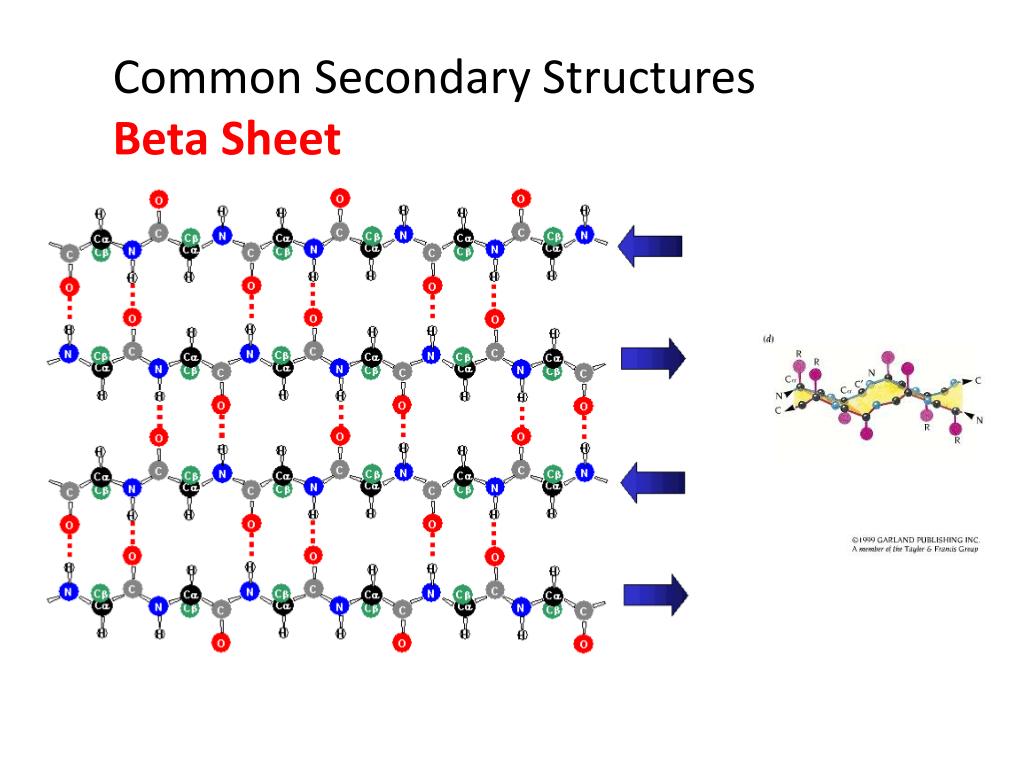
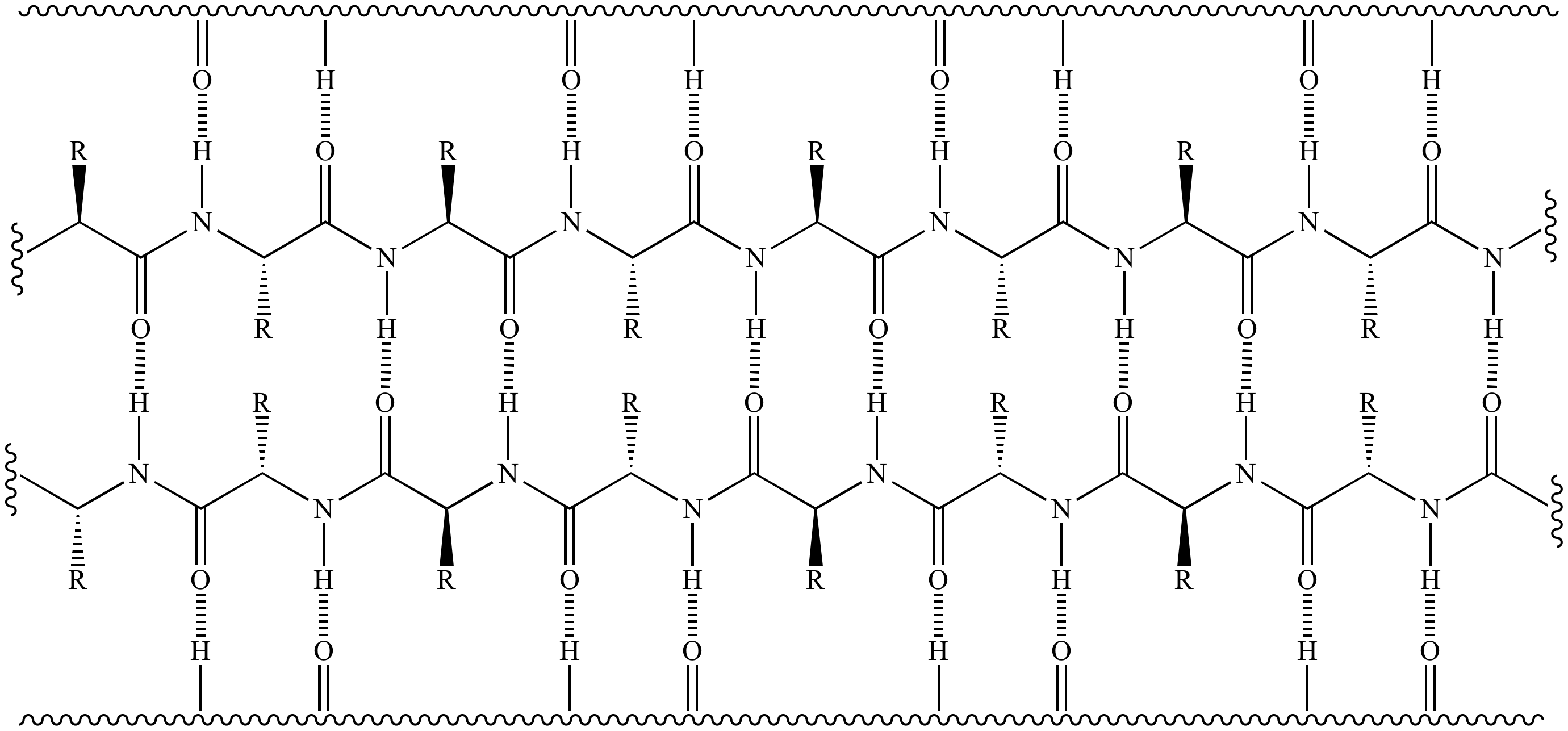
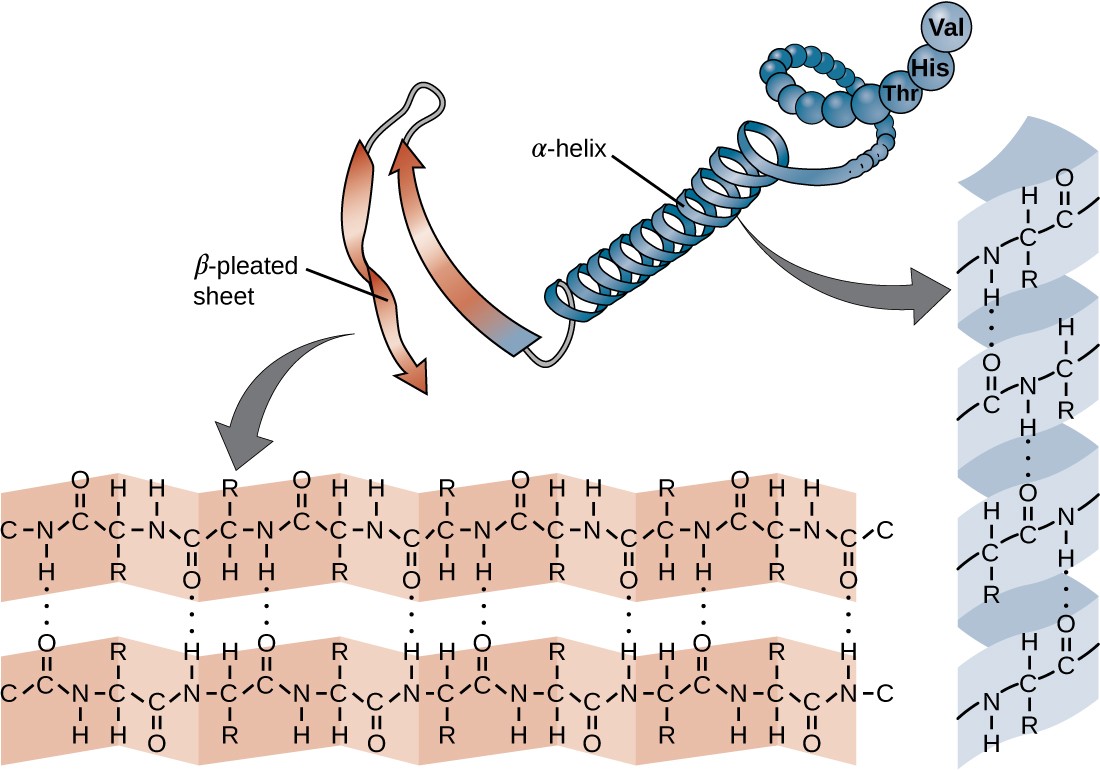
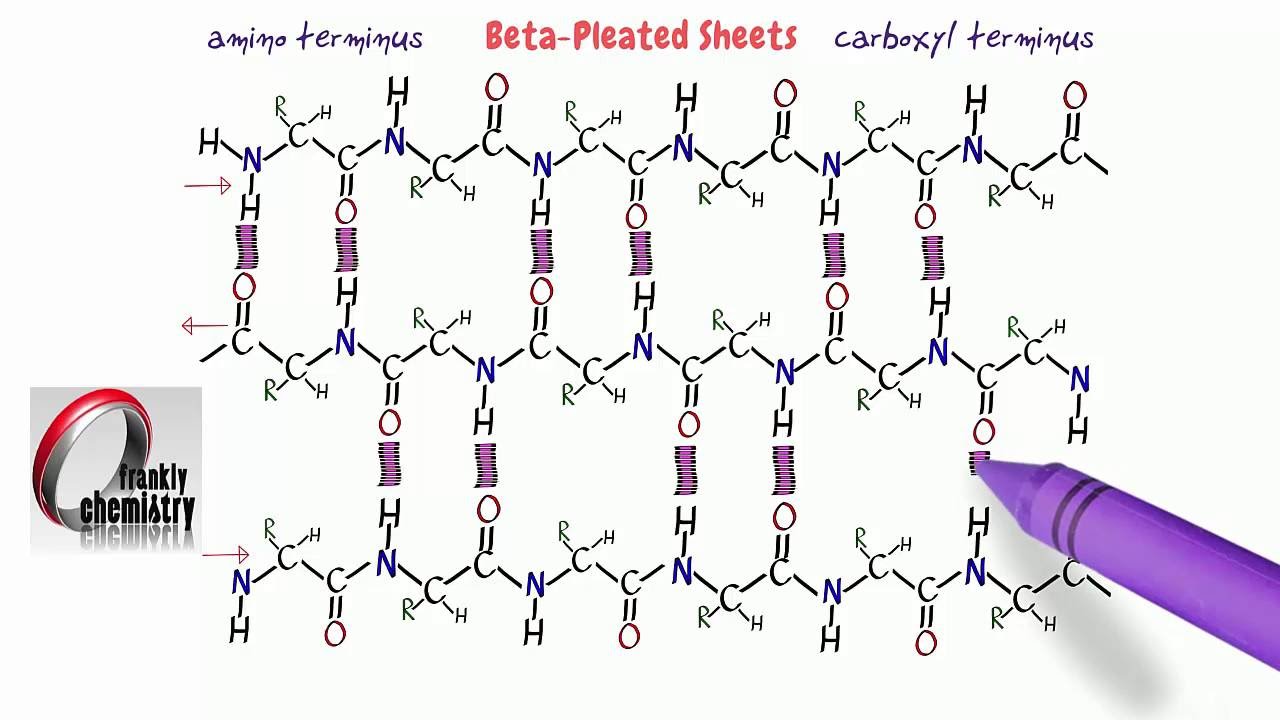
Beta Sheet Secondary Structure
Beta Sheet Secondary Structure - Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral.
Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone.
parallel beta sheet Cheaper Than Retail Price> Buy Clothing
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold.
Levels of protein structure secondary Biomacromolecular structures
Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone.
1. Secondary structure of protein, αhelix and βpleated sheet [118
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns.
PPT Protein Structure and Prediction PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. This structure occurs.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Beta sheet, betapleated sheet
Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are.
secondary structure alpha helix parallel antiparallel beta sheet .pdf
Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements.
7.4 Proteins Microbiology 201
Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and.
Amino Acids 8. The betapleated sheets secondary structure of Proteins
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns.
Beta pleated sheet Secondary structure of protein YouTube
Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate. Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns.
Secondary Structure Elements Typically Spontaneously Form As An Intermediate.
Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Web the secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups that make up the polypeptide backbone and causes the molecule to either bend and fold (beta pleated sheet) or spiral. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.