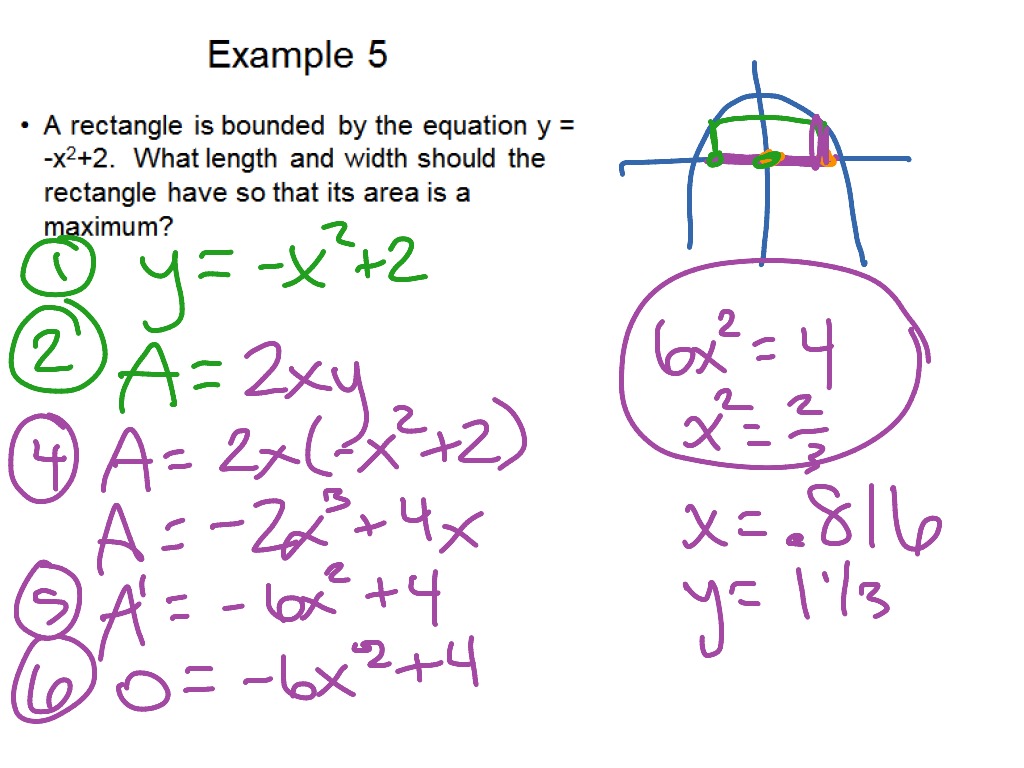
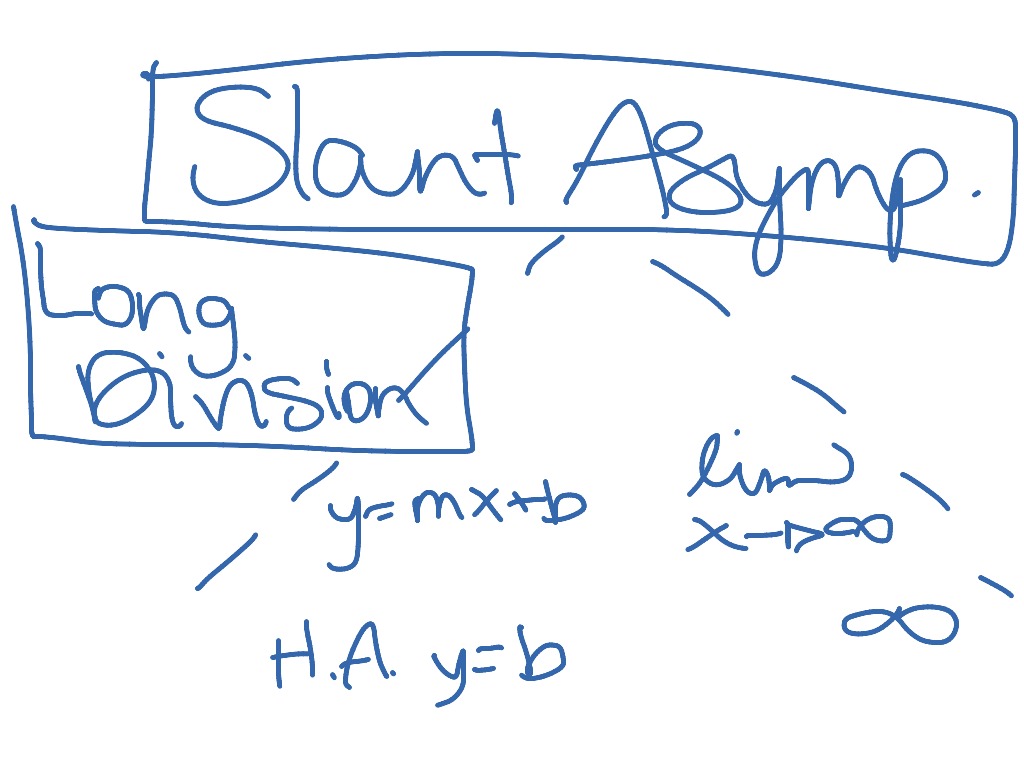
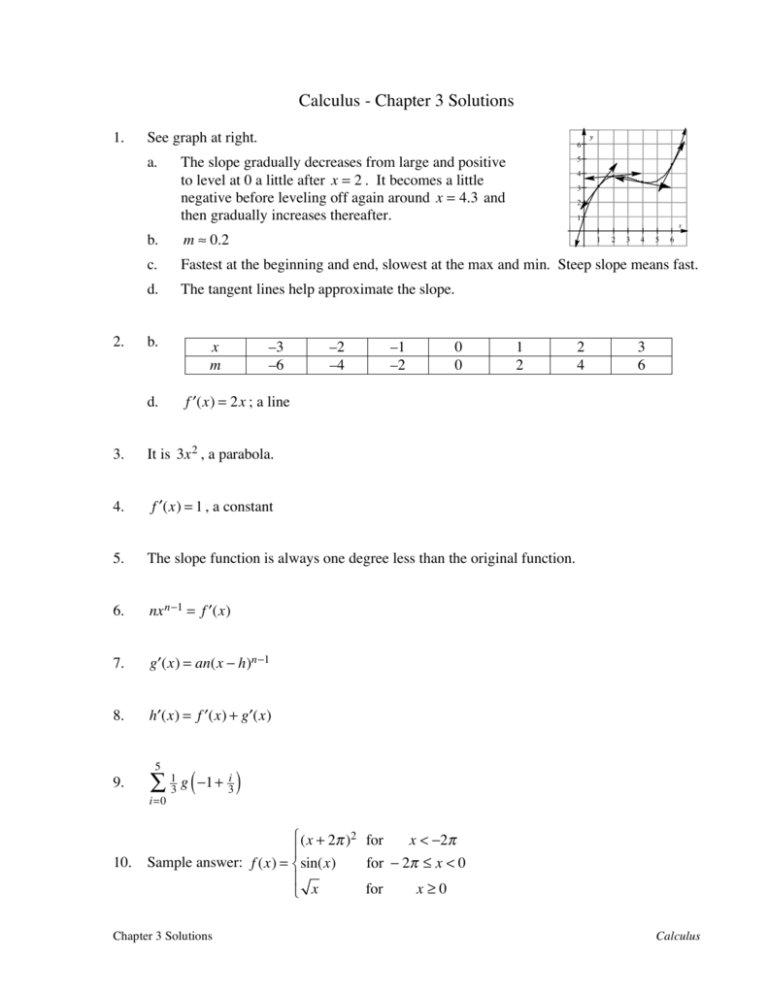
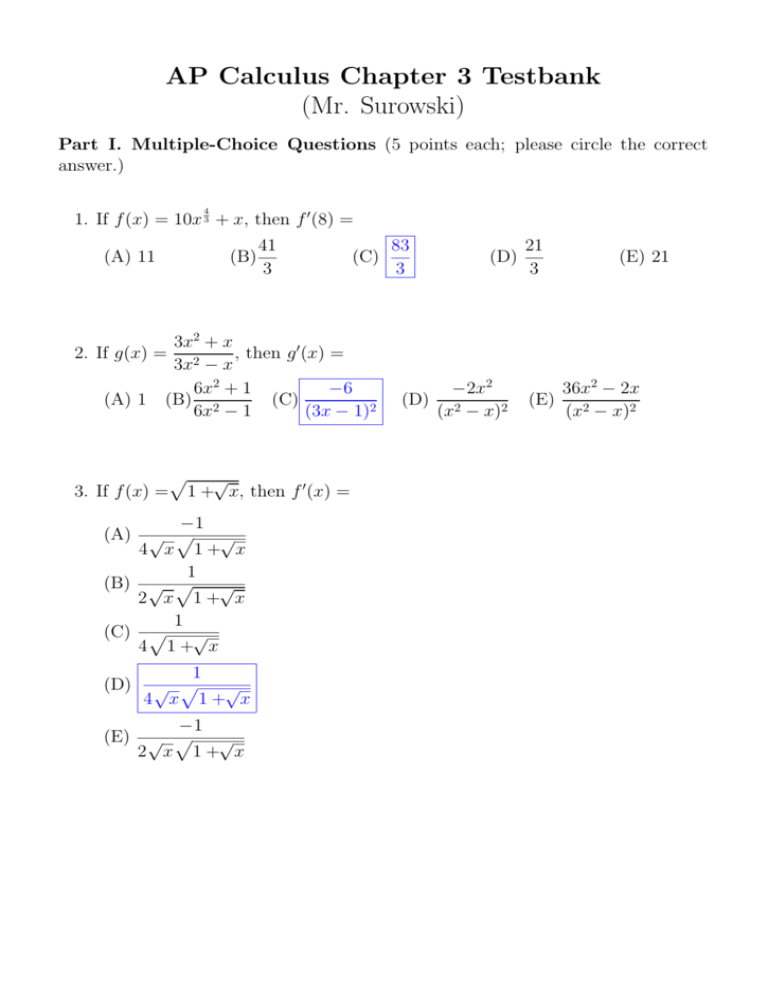
Calculus Chapter 3
Calculus Chapter 3 - As x → ± ∞, f(x) → − ∞ because of the negative coefficient. General theorem, intermediate forms with analytic geometry written by dr. We will also discuss how to find the equations. Web 3.3.2 apply the sum and difference rules to combine derivatives. 3.5 derivatives of trigonometric functions; As x approaches positive or negative infinity, f(x) decreases without bound: Click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test match created by ryan__valentino terms in this set (9) derivatives of trig functions derivatives of inverse trig functions derivative of natural log. Web what is calculus 3? Web learn calculus chapter 3 with free interactive flashcards. The following video provides an outline of all the topics you would expect to see in a typical multivariable calculus class (i.e., calculus 3, vector calculus, multivariate calculus).
An introduction to vectors professor leonard 733k subscribers subscribe 1.8m views 7 years ago calculus 3 (full length videos) calculus 3 lecture 11.1: Notes of the chapter 03: Calculus volume 2 publication date: 3.4 derivatives as rates of change; General theorem, intermediate forms with analytic geometry written by dr. Web 3.1 defining the derivative; Alternative form of the derivative at xc= : 3.3.4 use the quotient rule for finding the derivative of a quotient of. With expert solutions for thousands of practice problems, you. F(x) is a power function because it can be written as f(x) = 8x5.
With expert solutions for thousands of practice problems, you. Web calculus 3 lecture 11.1: Web 3.1 defining the derivative; General theorem, intermediate forms [bsc calculus 3rd chapter] what is in the this chapter? 3.15 y = 12x − 23 3… Click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test match created by ryan__valentino terms in this set (9) derivatives of trig functions derivatives of inverse trig functions derivative of natural log. Web learn calculus chapter 3 with free interactive flashcards. 3.4 derivatives as rates of change; The other functions are not power functions. * rolle's theorem * geometrical interpretation of rolle's theorem * the mean value.
Calculus Chapter 3 Day 9 & 10 ShowMe
Web derivative formulas through geometry | chapter 3, essence of calculus 3blue1brown 5.01m subscribers 2.4m views 5 years ago 3blue1brown series s2 e3 some common derivative formulas explained. As x approaches positive or negative infinity, f(x) decreases without bound: We will also discuss how to find the equations. 3.3.3 use the product rule for finding the derivative of a product.
Calculus Chapter 3 Day 8 ShowMe
( ) 0 ( ) lim x fx x fx fx ∆→ x +∆ − ′ = ∆ 2. Web calculus 3 lecture 11.1: 3.3.3 use the product rule for finding the derivative of a product of functions. We will also discuss how to find the equations. Web what is calculus 3?
Calculus 3 Chapter 15.4 YouTube
F(x) is a power function because it can be written as f(x) = 8x5. 3.15 y = 12x − 23 3… Applications of multivariable derivatives 0/500 mastery points tangent planes and local linearization quadratic approximations optimizing multivariable functions optimizing multivariable. 3.3.3 use the product rule for finding the derivative of a product of functions. The other functions are not power.
Bc Calculus Formula Sheet jenwiles
Web this chapter is generally prep work for calculus iii and so we will cover the standard 3d coordinate system as well as a couple of alternative coordinate systems. 3.2 the derivative as a function; 3.5 derivatives of trigonometric functions; General theorem, intermediate forms [bsc calculus 3rd chapter] what is in the this chapter? All the topics are covered in.
Calculus CPM question 33 YouTube
3.5 derivatives of trigonometric functions; 3.4 derivatives as rates of change; Definition of the derivative of a function: General theorem, intermediate forms [bsc calculus 3rd chapter] what is in the this chapter? As x approaches positive or negative infinity, f(x) decreases without bound:
PPT Calculus Chapter 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
3.3.3 use the product rule for finding the derivative of a product of functions. General theorem, intermediate forms with analytic geometry written by dr. 3.2 the derivative as a function; 3.3.4 use the quotient rule for finding the derivative of a quotient of. Calculus volume 2 publication date:
Calculus Chapter 3 Solutions
3.2 the derivative as a function; Web 3.3.2 apply the sum and difference rules to combine derivatives. Web derivative formulas through geometry | chapter 3, essence of calculus 3blue1brown 5.01m subscribers 2.4m views 5 years ago 3blue1brown series s2 e3 some common derivative formulas explained. Choose from 5,000 different sets of calculus chapter 3 flashcards on quizlet. Applications of multivariable.
Calculus Chapter 3.6 YouTube
General theorem, intermediate forms with analytic geometry written by dr. ( ) lim() xc f x fc f c → xc − ′ = −. Calculus volume 3 publication date: Web our resource for calculus, volume 3 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. As x approaches positive.
Calculus 3 Chapter 14.1 YouTube
Web derivative formulas through geometry | chapter 3, essence of calculus 3blue1brown 5.01m subscribers 2.4m views 5 years ago 3blue1brown series s2 e3 some common derivative formulas explained. * rolle's theorem * geometrical interpretation of rolle's theorem * the mean value. The other functions are not power functions. As x approaches positive or negative infinity, f(x) decreases without bound: Web.
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski)
Web this chapter is generally prep work for calculus iii and so we will cover the standard 3d coordinate system as well as a couple of alternative coordinate systems. The following video provides an outline of all the topics you would expect to see in a typical multivariable calculus class (i.e., calculus 3, vector calculus, multivariate calculus). General theorem, intermediate.
Raise Prices 3.6 F ′ (X) = 2X 3.7 (0, +∞) 3.8 A = 6 And B = −9 3.9 F″(X) = 2 3.10 A(T) = 6T 3.11 0 3.12 4X3 3.13 F ′ (X) = 7X6 3.14 F ′ (X) = 6X2 − 12X.
With expert solutions for thousands of practice problems, you. Calculus volume 2 publication date: 3.3.3 use the product rule for finding the derivative of a product of functions. 3.15 y = 12x − 23 3…
3.4 Derivatives As Rates Of Change;
We will also discuss how to find the equations. All the topics are covered in detail in our online calculus 3. Web what is calculus 3? Notes of the chapter 03:
Web Derivative Formulas Through Geometry | Chapter 3, Essence Of Calculus 3Blue1Brown 5.01M Subscribers 2.4M Views 5 Years Ago 3Blue1Brown Series S2 E3 Some Common Derivative Formulas Explained.
Definition of the derivative of a function: ( ) 0 ( ) lim x fx x fx fx ∆→ x +∆ − ′ = ∆ 2. Web 3.1 defining the derivative; General theorem, intermediate forms with analytic geometry written by dr.
As X → ± ∞, F(X) → − ∞ Because Of The Negative Coefficient.
3.2 the derivative as a function; Web calculus 3 lecture 11.1: Applications of multivariable derivatives 0/500 mastery points tangent planes and local linearization quadratic approximations optimizing multivariable functions optimizing multivariable. General theorem, intermediate forms [bsc calculus 3rd chapter] what is in the this chapter?