Chapter 14 Solids Liquids And Gases Answer Key
Chapter 14 Solids Liquids And Gases Answer Key - Use your textbook to complete each activity. Web a solid has definite volume and shape, a liquid has a definite volume but no definite shape, and a gas has neither a definite volume nor shape. Why is there no change in volume when pressure is applied to liquids and solids? Matter and thermal energy • section 2: Solids, liquids, and gases • section 1: Highly strong intermolecular forces between the molecules, leads to a definite volume in solids. Energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid. The molecules in liquids and solids are very close together already. Assume that p i 101 kpa and v i 10.0 l. Why do gases compress more easily than liquids and solids?
Web according to 14._____ law, if a sample of gas is kept at constant 15._____, the volume increases if the temperature is 16._____. Some answers have been filled in for you. Web solids, liquids, and gases google classroom which of the following phase transitions is illustrated in the diagram above? Melting a melting freezing b freezing vaporization c vaporization. Particles in this state of matter slide past each other and take the shape of their container giving it a definite volume. The term used to explain how hot or cold an object. Properties of fluids • section 3: A liquid becomes a gas. Web chapter 14 section 2 properties of fluids 5.0 (1 review) buoyancy click the card to flip 👆 the ability of a fluid to exert an upward force on an object immersed in it click the card to flip 👆 1 / 9 flashcards learn test match. The amount of energy needed to change a substance from a solid phase to a liquid phase is _____.
Web changes of state. Interpret a graphwhat is the pressure of the gas. Webdifference between solid liquid and gases; List uses for compressed gases. Melting a melting freezing b freezing vaporization c vaporization. Solve an equation use the equation p iv p fv. An explanation of how the particles in gases behave. Solids, liquids, and gases solids, liquids, and gases. The total energy of a material's particles. This state of matter fills whichever container is it in.
Directed Reading For Content Mastery Overview Motion Answer Key
Solve an equation use the equation p iv p fv. Use your textbook to complete each activity. Why do gases compress more easily than liquids and solids? Properties of fluids • section 3: The molecules of a solid are closely packed.
States of Matter (Solids, Liquids, Gases) and Solutions Editable
Charle's, pressure, decrease charles's measurements suggested that the 17.__________ of a gas would become zero at a temperature of. Matter and thermal energy • section 2: Some answers have been filled in for you. Interpret a graphwhat is the pressure of the gas. Why do gases compress more easily than liquids and solids?
Solids, Liquids and Gases Vocabulary Ninja
Oxygen for patients, anesthesia, barbeque grills. Solve an equation use the equation p iv p fv. Webdifference between solid liquid and gases; The molecules of a solid are closely packed. Interpret a graphwhat is the pressure of the gas.
Physics 102, Class 11 “The Atomic Nature of Matter” Physics 102
The molecules of a solid are closely packed. Web terms in this set (21) kinetic theory. An explanation of how particles in matter behave. Some answers have been filled in for you. The intermolecular forces are stronger than gases but weaker than solids.
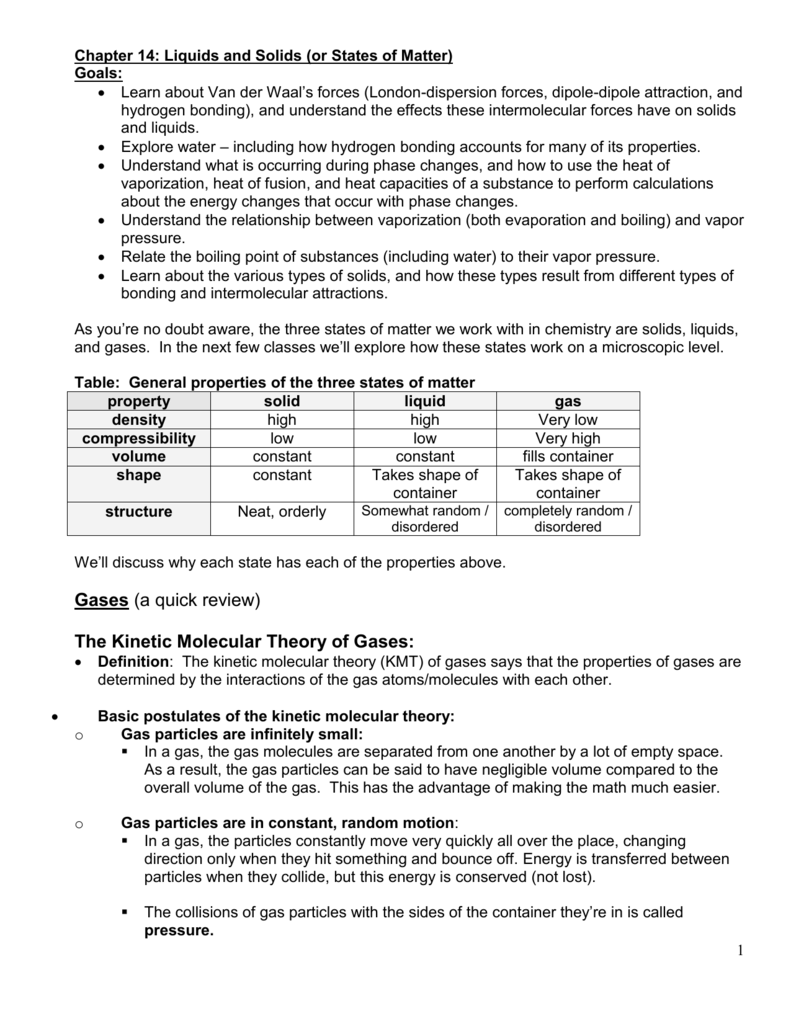
Chapter 14 Liquids and Solids (or States of Matter) Goals Learn
An explanation of how particles in matter behave. Gas molecules are very far apart. Melting a melting freezing b freezing vaporization c vaporization. The molecules of a solid are closely packed. The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility review questions 1.
30 Behavior Of Gases Worksheet Education Template
Webdifference between solid liquid and gases; Web solids, liquids, and gases google classroom which of the following phase transitions is illustrated in the diagram above? Some answers have been filled in for you. Temperature at which a solid begins to become a liquid. The three main forms of matter are called solid, liquids and gases.
Chapter 14 Solids Liquids and Gases Answer Key
Highly strong intermolecular forces between the molecules, leads to a definite volume in solids. Temperature at which a solid begins to become a liquid. Temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. Webdifference between solid liquid and gases; The intermolecular forces are stronger than gases but weaker than solids.
Chapter 16 Solids, Liquids, Gases
List uses for compressed gases. Fill in the table to compare and contrast solids, liquids, and gases. An explanation of how the particles in gases behave. Which of the following gases is used in refrigeration and in fire extinguishers? Web mcgraw hill chapter 14 solids liquids gases flashcards learn test match kinetic theory click the card to flip 👆 an.
Chapter 14, Solids, Liquids, and Gases Section 1 States of Matter
Particles in this state of matter slide past each other and take the shape of their container giving it a definite volume. A solid keeps it shape, a liquid takes the shape of its container and a gas fills its container. Charle's, pressure, decrease charles's measurements suggested that the 17.__________ of a gas would become zero at a temperature of..
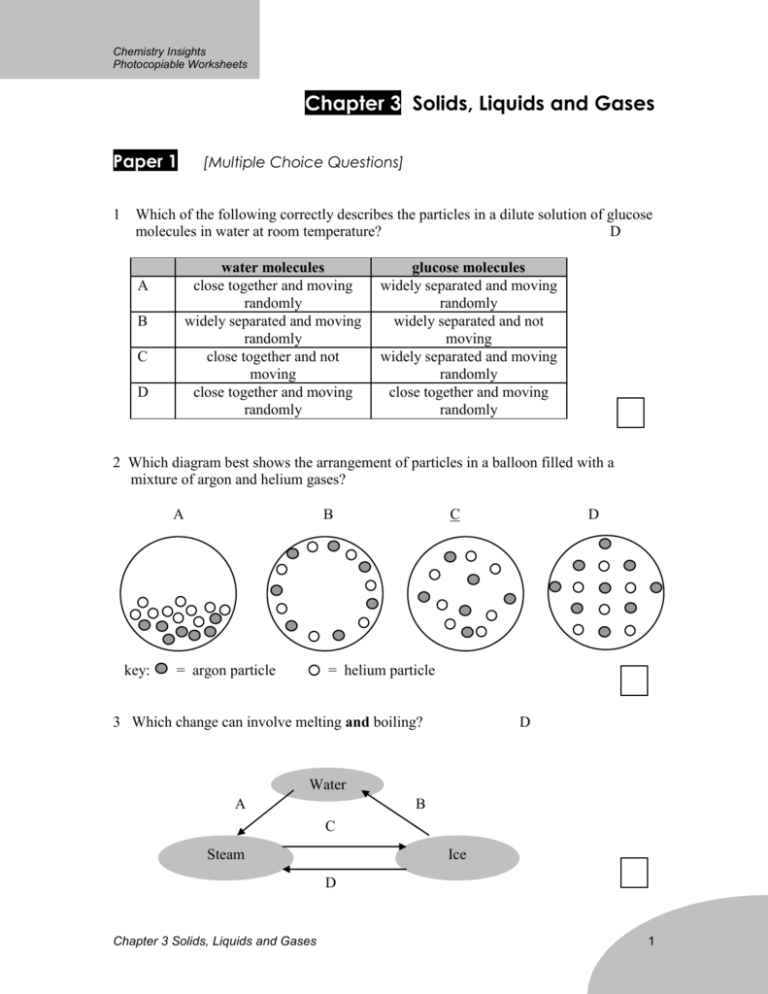
Chapter 3 Solids, Liquids and Gases
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. Use your textbook to complete each activity. The term used to explain how hot or cold an object. This chapter looks at key ideas and activities that can be used to help students learn about solids, liquids and gases, and understand that some. Interpret a graphwhat is the pressure of the.
Use Your Textbook To Complete Each Activity.
Web solids, liquids and gases definition. A liquid becomes a gas. The correct answer for each question is indicated by a. The intermolecular forces are stronger than gases but weaker than solids.
The Temperature At Which A Solid Becomes A Liquid.
The behavior of gases 14.1 compressibility review questions 1. The term used to explain how hot or cold an object. Web the ‘solids, liquids and gases’ chapter from that’s chemistry! Oxygen for patients, anesthesia, barbeque grills.
Properties Of Fluids • Section 3:
A.) nitrous oxide b.) krypton c.) xenon d.) radon correct answer. Solids, liquids, and gases solids, liquids, and gases. The molecules in liquids and solids are very close together already. Why do gases compress more easily than liquids and solids?
The Change From Solid To Liquid Usually Does Not.
Temperature at which a solid begins to become a liquid. Web changes of state. A solid keeps it shape, a liquid takes the shape of its container and a gas fills its container. Charle's, pressure, decrease charles's measurements suggested that the 17.__________ of a gas would become zero at a temperature of.