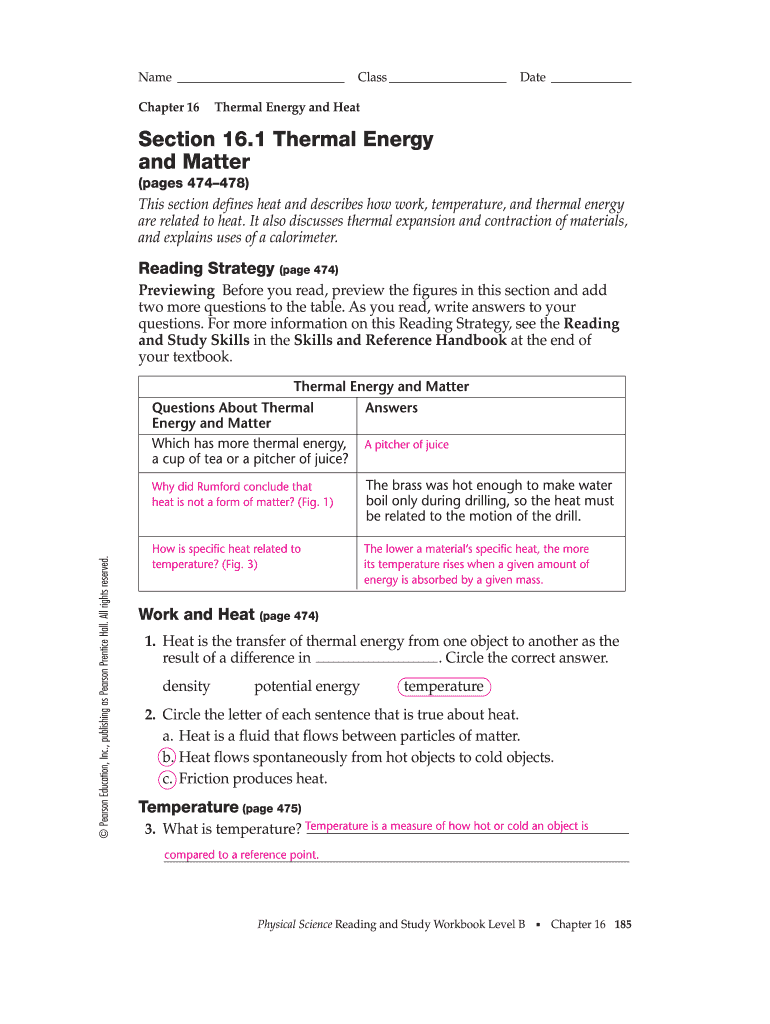
Chapter 16 Thermal Energy And Heat
Chapter 16 Thermal Energy And Heat - Thermometers what is an example of thermal expansion ? Count rumford rumford studied the process of drilling holes in the barrels of cannons. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by one degree celsius. An increase in volume of a material due to a temperature increase. Chapter 16 thermal energy and heat. B.heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects. Web scientists define heat as thermal energy transferred between two systems at different temperatures that come in contact. A measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to a reference point. Web terms in this set (63) heat. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by one degree celsius.
A measure of how hot. Conduction can occur between materials that are not touching. Click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 17 celsius kelvin fahrenheit click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn. Web terms in this set (63) heat. Mass, temperature, and phase (solid, liquid, gas) what does thermal energy depend on? The two main types of heat engines are the _____ and the _____ combustion. Select the web sample in the catalogue. In the 1700’s most scientists thought that heat was a fluid called caloric that. Chapter 16 thermal energy and heat. The transfer of thermal energy from one body of matter to another because of a temperature difference.
Chapter 16 thermal energy and heat. Web what is thermal energy? Web thermal energy is related to the movement of particles in an object; Web physical science chapter 16 term 1 / 17 which of the following is a unit of temperature? Web name two variables that affect the thermal energy of an object. Web summary 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects. Web the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a difference in temperature. 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of temp. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by one degree celsius. Web terms in this set (63) heat.
PPT Chapter 16 Thermal Energy and Heat PowerPoint Presentation
Web the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a difference in temperature. 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of temp. Depends on mass, temperature, and phase of an object. D.the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another is heat… Web terms in this.
️Thermodynamics Worksheet Answer Key Free Download Gambr.co
A measure of how hot. Depends on mass, temperature, and phase of an object. Web name two variables that affect the thermal energy of an object. 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of temp. In the 1700’s most scientists thought that heat was a fluid called caloric that.
Difference Between Heat and Thermal Energy Difference Between
How do the temperature increases of different materials depend on their specific heats? This motion can generate heat. Web the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a difference in temperature. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by one degree celsius. I can describe the differences in.
PPT Chapter 16 Thermal Energy and Heat PowerPoint Presentation, free
Thermal energy is transferred without transfer of matter. Conduction can occur between materials that are not touching. How do the temperature increases of different materials depend on their specific heats? Heat is written with the symbol q or q, and it has units of joules ( \text j j ). Web the transfer of thermal energy when particles of a.
PPT Chapter 16 Thermal Energy and Heat PowerPoint Presentation, free
This motion can generate heat. Depends on mass, temperature, and phase of an object. Enter all required information in the necessary fillable areas. Thermometers what is an example of thermal expansion ? Click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 17 celsius kelvin fahrenheit click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn.
How should governments subsidize cleanenergy heating?
Web scientists define heat as thermal energy transferred between two systems at different temperatures that come in contact. Thermometers what is an example of thermal expansion ? An increase in volume of a material due to a temperature increase. Instrument used to measure thermal energy. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material.
Section 16 1 Thermal Energy And Matter Fill Online, Printable
Depends on mass, temperature, and phase of an object. Web summary 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects. What causes thermal expansion of an object when it is heated? Web scientists define heat as thermal energy transferred between two systems at different temperatures that come in contact. How do the temperature increases of.
Thermal Energy & Heat Transfer Middle School Science Unit Teaching
Thermometers what is an example of thermal expansion ? Conduction can occur between materials that are not touching. A measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to a reference point. The process occurred in water so that the metal would not melt due to the heat. B.heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects.
Chapter 16 Thermal Energy and Heat
Web thermodynamics is the study of conversions betwe= en _____ energy and other forms of energy. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a temperature difference. The two main types of heat engines are the _____ and the _____ combustion. The transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a.
PPT Chapter 16 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6516821
A measure of how hot or cold an object is compared to a reference point. Web physical science chapter 16 term 1 / 17 which of the following is a unit of temperature? The transfer of thermal energy from one object to another because of a temperature difference. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram.
Click The Card To Flip 👆 Definition 1 / 17 Celsius Kelvin Fahrenheit Click The Card To Flip 👆 Flashcards Learn.
Web the transfer of thermal energy when particles of a fluid move from one place to another. A.heat is a fluid that flows between particles of matter. The process occurred in water so that the metal would not melt due to the heat. Web summary 16.1 thermal energy and matter heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects.
Web Terms In This Set (63) Heat.
The two main types of heat engines are the _____ and the _____ combustion. Web what is thermal energy? B.heat flows spontaneously from hot objects to cold objects. Thermal energy is transferred without transfer of matter.
How Do The Temperature Increases Of Different Materials Depend On Their Specific Heats?
In the 1700’s most scientists thought that heat was a fluid called caloric that. A measure of how hot. Select the web sample in the catalogue. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by one degree celsius.
Count Rumford Rumford Studied The Process Of Drilling Holes In The Barrels Of Cannons.
Temperature is related to the average kinetic energy. What principle explains how a calorimeter is used to measure the specific heat. An increase in volume of a material due to a temperature increase. Circulation of a fluid in a loop as the fluid alternately heats up and cools down.