Chapter 4 Linear Motion Answer Key
Chapter 4 Linear Motion Answer Key - The speed of a plane can be described as 300. Web [download] chapter 4 linear motion answer key | updated! 10.2 kinematics of rotational motion; 10.3 dynamics of rotational motion: Web determine which of the following moving objects obey the equations of projectile motion developed in this chapter. All of the above (miles per hour; Web the pavement of the surface of earth define speed. Web western sierra collegiate academy Web test match created by gmsalzer terms in this set (42) t/f? Quantity in physics that has both magnitude and direction.
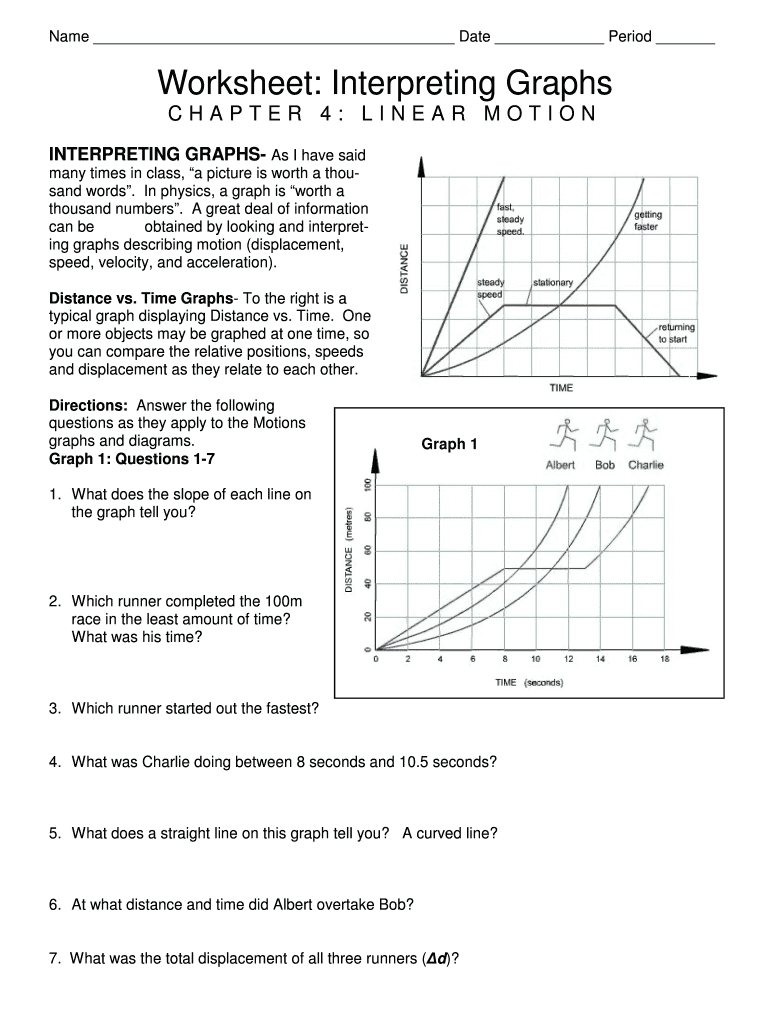
4.1 the racing cars in the indy 500 move relative to the track. True an object is ____ if. Web highlights learning objectives in this section, you will: Web 5099 chapter 4 test linear motion answer key | added by request 5971 kb/s 11680 chapter 4 test linear motion answer key | checked 2867 kb/s 3639 3 linear motion 3 linear motion. Web worksheet interpreting graphs chapter 4 linear motion form. Web determine which of the following moving objects obey the equations of projectile motion developed in this chapter. Web which is different from v→(3.0s)=81.0i^m/s.v→(3.0s)=81.0i^m/s. Web $40 40 m/s $50 50 m/s 5 s 0 m/s 5 s 10 m/s; Web equations of motion. Chapter 4 linear motion 47 if a cheetah can maintain a constant speed of 25 m/s, it will cover 25 meters every second.
Web one possible unit of speed is. Speed = distance / time how is the slash symbol read in km/h per what is true of instantaneous speed? If a, b, and care not zero, then the velocity function must be linear. Web which is different from v→(3.0s)=81.0i^m/s.v→(3.0s)=81.0i^m/s. We are not affiliated with any. What is a vector quantity? True an object is ____ if. All of the above (miles per hour; Web [download] chapter 4 linear motion answer key | updated! Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant.
Chapter 4 by jessfett
Velocity divided by the time interval. Kilometers per hour) acceleration is defined as the change in. Web the speed of an object and a specification of its direction of motion. Chapter 4 linear motion 47 if a cheetah can maintain a constant speed of 25 m/s, it will cover 25 meters every second. The rate at which velocity changes with.
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Linear Motion SmartStudy 思敏特培训中心
Kilometers per hour) acceleration is defined as the change in. Web test match created by gmsalzer terms in this set (42) t/f? What is a vector quantity? Write and interpret an equation for a linear function. How fast an object is going complete the following equation:
30 Motion Graphs Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
What is a vector quantity? All of the above (miles per hour; Web one possible unit of speed is. Write and interpret an equation for a linear function. Web this worksheet interpreting graphs chapter 4 linear motion answers, as one of the most vigorous sellers here will definitely be along with the best options to review.
Interpreting Graphs Answer Key Form Fill Out and Sign Printable PDF
Web $40 40 m/s $50 50 m/s 5 s 0 m/s 5 s 10 m/s; Web equations of motion. Web chapter 4 linear motion answer key introduction: What is a vector quantity? Write and interpret an equation for a linear function.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion Answer Key Elizabeth
Web $40 40 m/s $50 50 m/s 5 s 0 m/s 5 s 10 m/s; 10.3 dynamics of rotational motion: V → = v → 0. At this rate, how far. Chapter 4 linear motion 47 if a cheetah can maintain a constant speed of 25 m/s, it will cover 25 meters every second.
30 Motion Graphs Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
A rocket leaves the launch pad. At this rate, how far. Web determine which of the following moving objects obey the equations of projectile motion developed in this chapter. The acceleration vector is constant and doesn’t change with time. Web $40 40 m/s $50 50 m/s 5 s 0 m/s 5 s 10 m/s;
the domino effect Physics
We are not affiliated with any. A rocket leaves the launch pad. V → = v → 0. Web worksheet interpreting graphs chapter 4 linear motion form. Velocity, and acceleration, and move quickly to chapter 4.
30 Motion Graphs Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
Web the speed of an object and a specification of its direction of motion. Web if your average speed is 30 kilometers per hour and your trip took 1 hour, what was the total distance covered? Web highlights learning objectives in this section, you will: V → = v → 0. Web introduction to rotational motion and angular momentum;
30 Motion Graphs Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
Web determine which of the following moving objects obey the equations of projectile motion developed in this chapter. Web 5099 chapter 4 test linear motion answer key | added by request 5971 kb/s 11680 chapter 4 test linear motion answer key | checked 2867 kb/s 3639 3 linear motion 3 linear motion. A rocket leaves the launch pad. Web chapter.
30 Motion Graphs Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
If a, b, and care not zero, then the velocity function must be linear. What is a vector quantity? Kilometers per hour) acceleration is defined as the change in. Web this worksheet interpreting graphs chapter 4 linear motion answers, as one of the most vigorous sellers here will definitely be along with the best options to review. All of the.
The Acceleration Vector Is Constant And Doesn’t Change With Time.
How fast an object is going complete the following equation: 10.2 kinematics of rotational motion; Web test match created by gmsalzer terms in this set (42) t/f? The rate at which velocity changes with.
Web The Pavement Of The Surface Of Earth Define Speed.
Web introduction to rotational motion and angular momentum; 4.1 the racing cars in the indy 500 move relative to the track. Velocity divided by the time interval. All of the above (miles per hour;
Web $40 40 M/S $50 50 M/S 5 S 0 M/S 5 S 10 M/S;
A rocket leaves the launch pad. True an object is ____ if. Kilometers per hour) acceleration is defined as the change in. 35 answer in order to use d=vt, there must be no acceleration (in other words.
Web [Download] Chapter 4 Linear Motion Answer Key | Updated!
Web equations of motion. Web the speed of an object and a specification of its direction of motion. At this rate, how far. 10.3 dynamics of rotational motion: