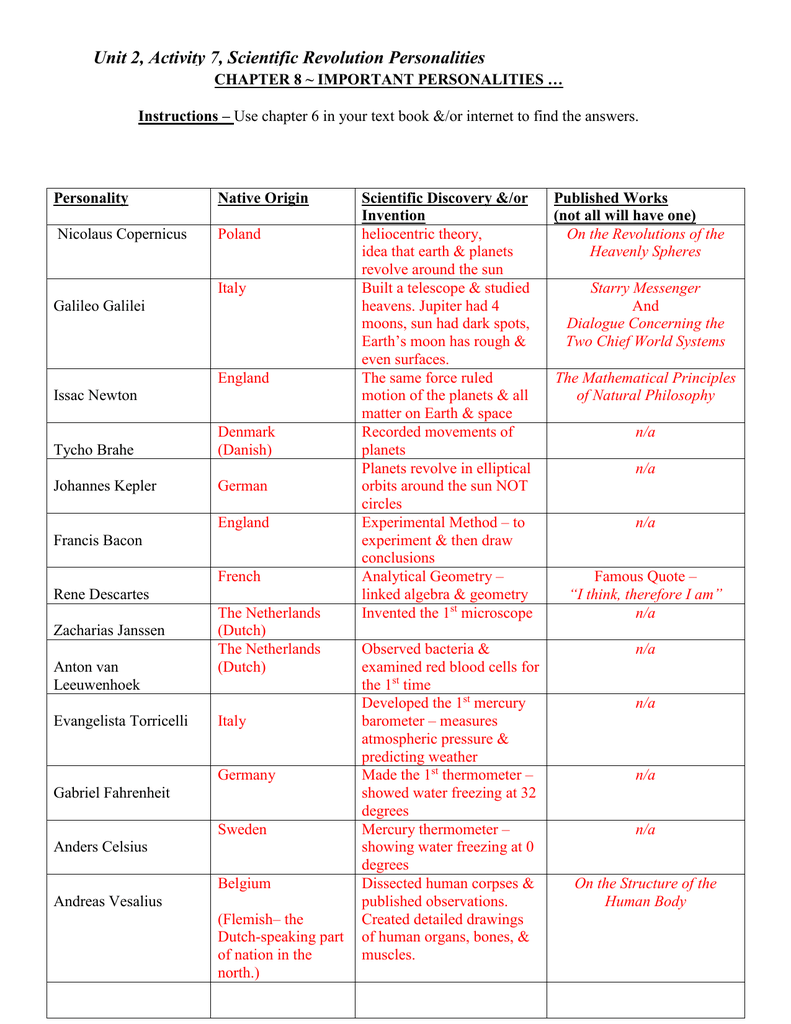
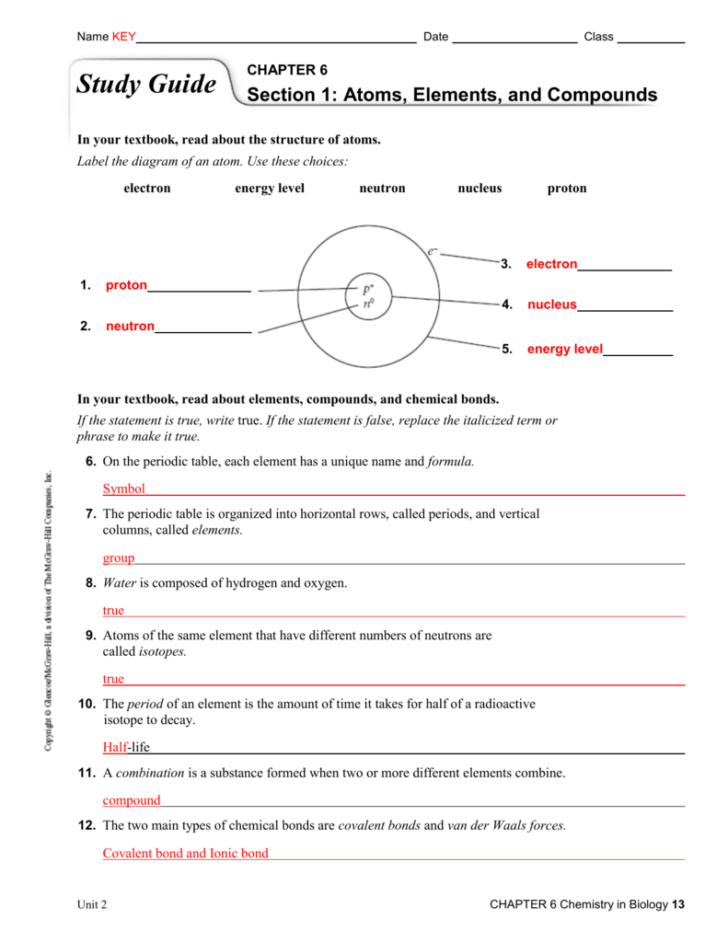
Chapter 6 Section 1 Price Controls Worksheet Answers
Chapter 6 Section 1 Price Controls Worksheet Answers - Legal maximum of a price (pc) price floor. Web chapter 6 section 1 price controls worksheet answers. Chapter 6, section 1 price: Price controls flashcards | chegg.com. 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve _______ by the amount of the tax. 3.4 price ceilings and price. Web web worksheet has about 28 questions covering supply and demand including price controls (ceilings and floors). What is the purpose of rent control? Price _______ when a surplus exists *.
Chapter 6 with answers 1. Web sectionx'z price controls fill in the blanks in questions 1 and 2 with the correct words. Price _______ when a surplus exists *. Because market prices are set by the intersection of supply (s) and demand (d), as long as the equilibrium price is below the price ceiling, the price ceiling. Supply and demand together in a market, supply and demand work together to determine the price of a good. What is the purpose of rent control? ________ ____________ is legally established. 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; Web web [view] chapter 6 section 1 price controls answer key | latest! At the equilibrium point, what is balanced with supply?
Legal maximum of a price (pc) price floor. Web correct answer (s) 1.) move their business to countries not bound by minimum wage law (for a large firm, the logistical costs of offshoring may be outweighed by the savings in labor costs.) 2.) use machinery instead. A price ceiling example—rent control. Which two groups accept an equilibrium price? Law (police) that sets a price other than the equilibrium price that would normally exist in the market. You must use these terms in your answer: What is the condition of the market when supply and demand are not balanced? A price ceiling is a legislated price jr s (2 w which legal trades cannot be made. Web terms in this set (24) _____________ _____________ are an attempt to set, or manipulate, prices through govt. Used to raise revenue for pubic purposes and to influence market.
Chapter 4c
3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; At equilibrium, the quantity of a good that is bought and sold is the _____ quantity and the price at which the good is bought and sold is the _____ price *. What happens at the point where buyers and sellers agree? Web worksheet has about 28 questions covering supply.
Variables and Controls Guided Practice Worksheet PDF & Digital
Web answer the following questions and complete the tasks in each section as described below. 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; ________ ____________ is legally established. Law (police) that sets a price other than the equilibrium price that would normally exist in the market. How does a shortage affect the price of an item?
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Roman Republic Worksheet Answers worksheet
Correct answer (s) 1.) there will be a surplus of milk. 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: Because market prices are set by the intersection of supply (s) and demand (d), as long as the equilibrium price is below the price ceiling, the price ceiling. Price controls flashcards | chegg.com. What happens at the point where buyers and sellers.
31 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Scientific Revolution Worksheet Answers
You must use these terms in your answer: Web 1 explain how supply and demand create equilibrium. At equilibrium, the quantity of a good that is bought and sold is the _____ quantity and the price at which the good is bought and sold is the _____ price *. Web web worksheet has about 28 questions covering supply and demand.
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Scientific Revolution Worksheet Answers
Web web [view] chapter 6 section 1 price controls answer key | latest! Correct answer (s) 1.) there will be a surplus of milk. Web correct answer (s) 1.) move their business to countries not bound by minimum wage law (for a large firm, the logistical costs of offshoring may be outweighed by the savings in labor costs.) 2.) use.
31 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Scientific Revolution Worksheet Answers
Web terms in this set (9) price control. Supply and demand together in a market, supply and demand work together to determine the price of a good. How does a shortage affect the price of an item? At the equilibrium point, what is balanced with supply? A price ceiling is a legislated price jr s (2 w which legal trades.
Chemistry In Biology Chapter 6 Worksheet Answers —
Price _______ when a surplus exists *. You must use these terms in your answer: Used to raise revenue for pubic purposes and to influence market. A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve _______ by the amount of the tax. Chapter 6 with answers 1.
Chapter 6 Section 1
How does a shortage affect the price of an item? Chapter 6, section 1 price: Chapter 6 with answers 1. Supply and demand together in a market, supply and demand work together to determine the price of a good. 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity:
Integrated Science I Chapter 6 Section 1 & 2 Quiz Review Give a
What is the condition of the market when supply and demand are not balanced? It is easier for sellers to. Web 1 explain how supply and demand create equilibrium. A price ceiling example—rent control. You must use these terms in your answer:
The Americans Chapter 6 Section 1 by jennifer hwang Issuu
Web chapter 6 section 1 price controls worksheet answers. Legal minimum of a price. Discuss have students explain the idea of price. Web terms in this set (9) price control. Web web [view] chapter 6 section 1 price controls answer key | latest!
A Price Ceiling Is A Legislated Price Jr S (2 W Which Legal Trades Cannot Be Made.
3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; Supply and demand together in a market, supply and demand work together to determine the price. Web terms in this set (24) _____________ _____________ are an attempt to set, or manipulate, prices through govt. A price ceiling is a legislated price jr s (2 w which legal trades cannot be made.
Web Sectionx'z Price Controls Fill In The Blanks In Questions 1 And 2 With The Correct Words.
Web worksheet has about 28 questions covering supply and demand including price controls (ceilings and floors). You must use these terms in your answer: Discuss have students explain the idea of price. Which two groups accept an equilibrium price?
Price _______ When A Surplus Exists *.
Supply and demand together in a market, supply and demand work together to determine the price of a good. What is the purpose of rent control? Web web worksheet has about 28 questions covering supply and demand including price controls (ceilings and floors). How does a shortage affect the price of an item?
At Equilibrium, The Quantity Of A Good That Is Bought And Sold Is The _____ Quantity And The Price At Which The Good Is Bought And Sold Is The _____ Price *.
Web web [view] chapter 6 section 1 price controls answer key | latest! Legal maximum of a price (pc) price floor. Because market prices are set by the intersection of supply (s) and demand (d), as long as the equilibrium price is below the price ceiling, the price ceiling. 3.4 price ceilings and price.