Chemistry Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key
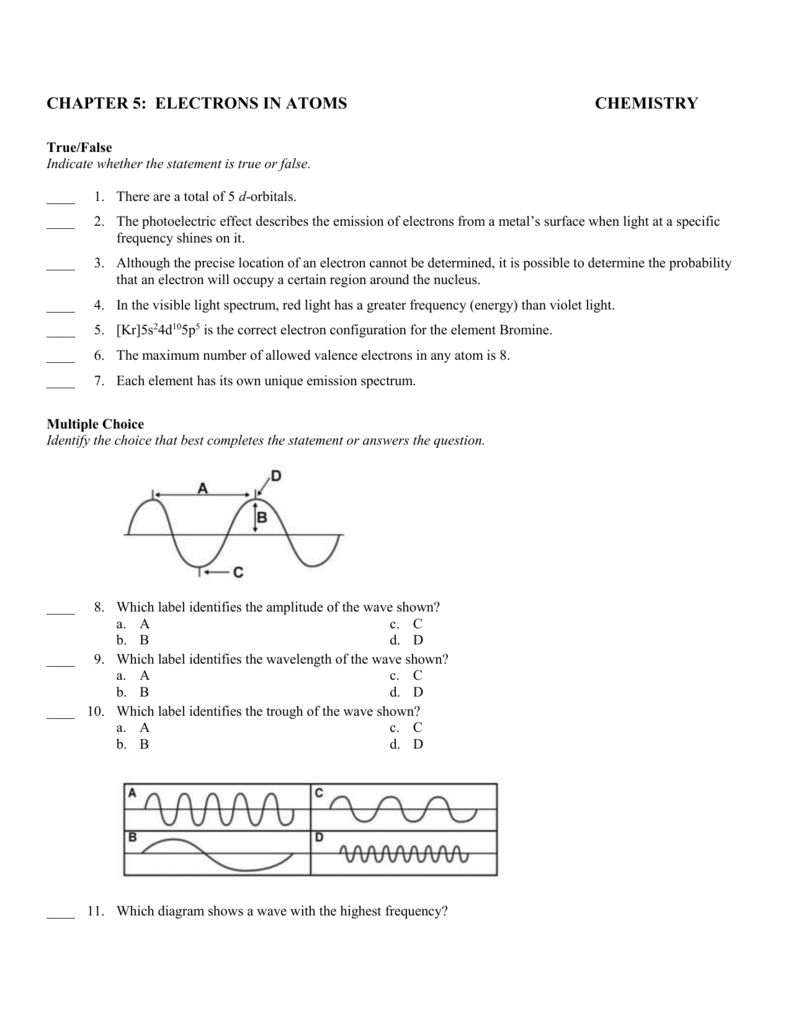
Chemistry Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key - Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. The height of a wave from the origin to a crest,or from the origin to a trough. The energy of the hot body. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the. Web chapter 5 electrons in atoms answers 5.3. No two electrons with the same spin can be found in the. Atoms are made of extremely tiny particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Web the pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four. Web chemistry chapter 5 electrons in atoms term 1 / 51 difference between ground state and the excited state of an electron? Web amplitude ____ is the _______, which is equivalent to one wave per second.
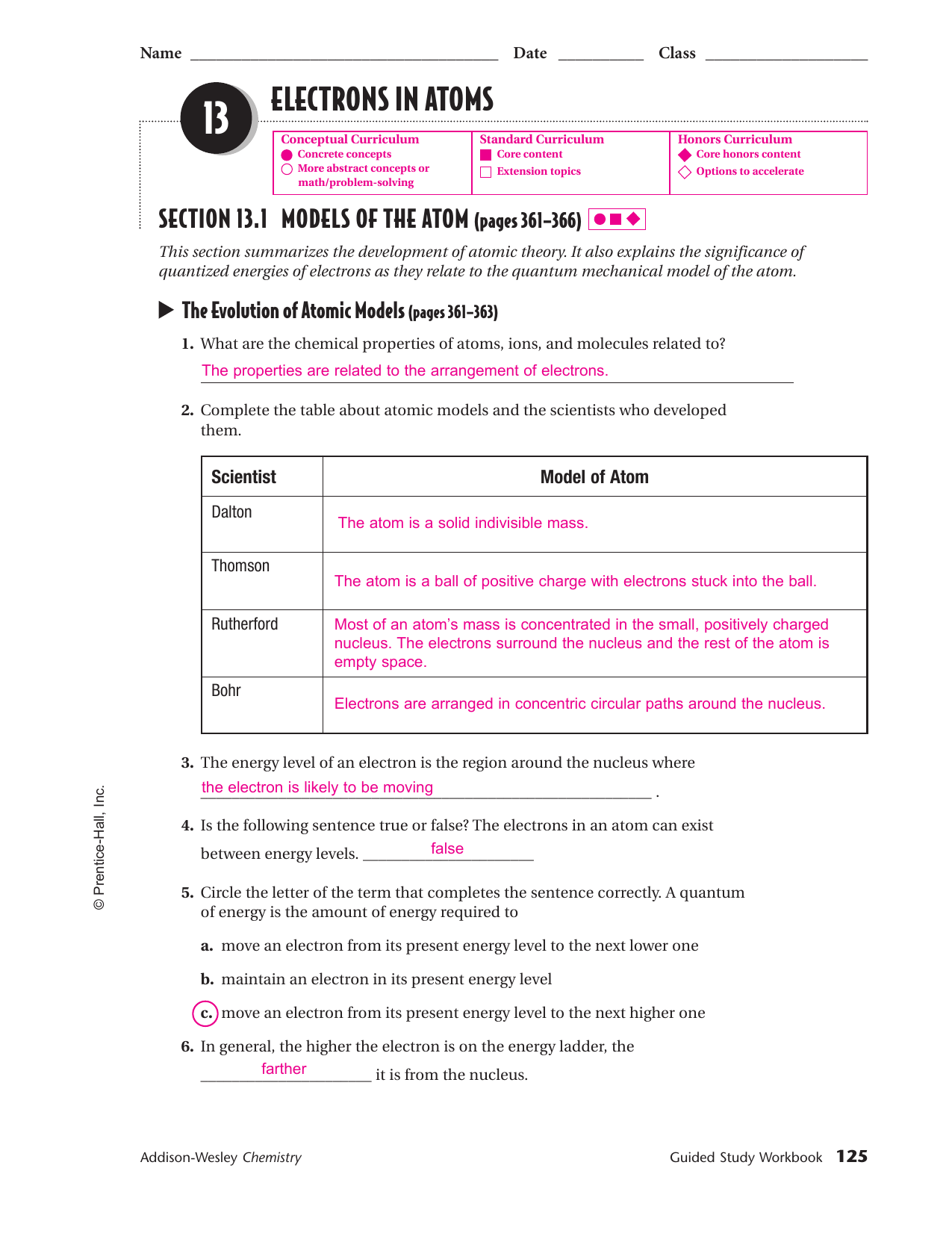
Web the structures are very similar. Matter and change chapter 5: Web start studying chapter 5: Electrons in atoms in this chapter: In the model mode, each electron group occupies the same amount of space, so the bond angle. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the. Bonding orbitals result in holding two or more. Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. Web chemistry chapter 5 electrons in atoms term 1 / 51 difference between ground state and the excited state of an electron?
Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. Web amplitude ____ is the _______, which is equivalent to one wave per second. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Web the structures are very similar. A set of frequencies of electromagnetic waves given off by atoms of an element; Web chapter 5 electrons in atoms answers 5.3. In the model mode, each electron group occupies the same amount of space, so the bond angle. No two electrons with the same spin can be found in the. Web start studying chapter 5: Both are orbitals that can contain two electrons.
Chapter 5 Assessment, solution manual,Electrons in Atoms, glencoe
Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. Web amplitude ____ is the _______, which is equivalent to one wave per second. Electrons in atoms 5.1 properties of light check your understanding 1. The most valence electrons for any element is 8. Web 1 / 45 the si unit of frequency click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test.
Electrons In Atoms Worksheet Answers Chapter 5 Breadandhearth
Web chemistry chapter 5 quiz: Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. What are the general properties of light? Atoms are made of extremely tiny particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The energy of the hot body.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key Chemistry
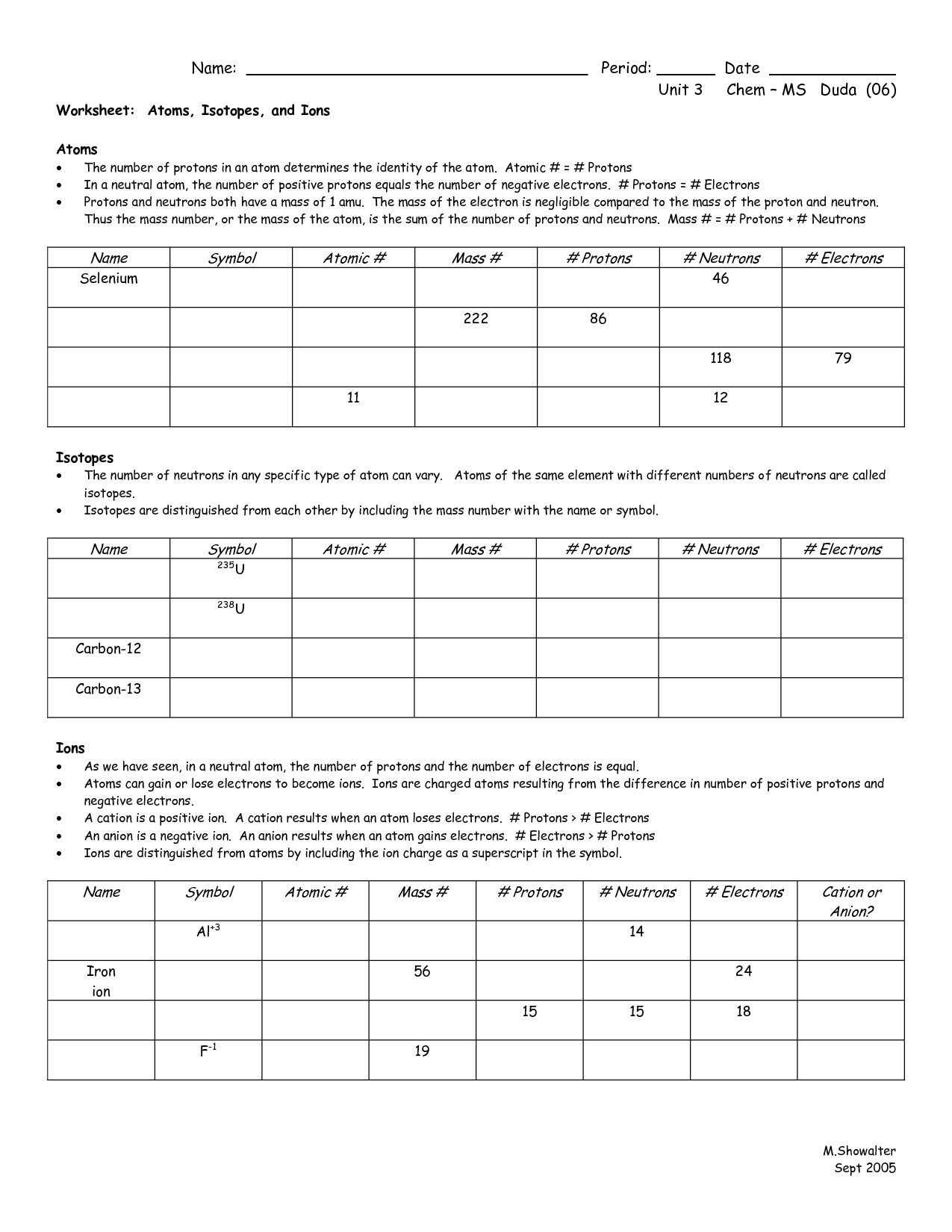
A hot object would emit electromagnetic energy in a continuous fashion. Web 32 terms · n= → number of sub levels, n^2 → number of orbitals, 2n^2 → number of electrons in each en…, energy level is →. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the. Matter and change chapter.
chapter 5 electrons in atoms chemistry
Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the. Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. Both are orbitals that can contain two electrons. A hot object would emit electromagnetic energy in a continuous fashion.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key THE PREMIER FEMALE DJ OF LOS
Electrons in atoms in this chapter: Web chapter 5 electrons in atoms answers 5.3. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Web this online broadcast electrons in atoms chapter 5 answer key can be one of the options to accompany you considering. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible.
Chapter 5 electrons in atoms
What are the general properties of light? Web this online broadcast electrons in atoms chapter 5 answer key can be one of the options to accompany you considering. Web the pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four. No two electrons with the same spin can be found in.
16 Molecules And Atoms Worksheet Answer Key /
Web chemistry chapter 5 electrons in atoms term 1 / 51 difference between ground state and the excited state of an electron? Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. What are the general properties of light? Web amplitude ____ is the _______, which is equivalent to one wave per second. The energy of the hot body.
5 1 Light And Quantized Energy Worksheet Answers
Web chapter 5 electrons in atoms answers 5.3. In the model mode, each electron group occupies the same amount of space, so the bond angle. Both are orbitals that can contain two electrons. The most valence electrons for any element is 8. Web the pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key THE PREMIER FEMALE DJ OF LOS
What are the general properties of light? Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. A hot object would emit electromagnetic energy in a continuous fashion. Both are orbitals that can contain two electrons. Web this online broadcast electrons in atoms chapter 5 answer key can be one of the options to accompany you considering.
10+ Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Answer Key WilliamMiran
Hertz, frequency a (n) _____ is the minimum. Web start studying chapter 5: The energy of the hot body. Web the pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four. Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the.
Web Chemistry Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms Term 1 / 51 Difference Between Ground State And The Excited State Of An Electron?
A hot object would emit electromagnetic energy in a continuous fashion. Matter and change chapter 5: Web each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available, it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the. Web chemistry chapter 5 quiz:
Bonding Orbitals Result In Holding Two Or More.
No two electrons with the same spin can be found in the. The energy of the hot body. Web amplitude ____ is the _______, which is equivalent to one wave per second. Web test match created by chloecourant terms in this set (27) why was rutherford's model of the atom known as the planetary.
What Are The General Properties Of Light?
Web chapter 5 electrons in atoms answers 5.3. The most valence electrons for any element is 8. Web 1 / 45 the si unit of frequency click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test match created by tanya_myers52 terms in this set (45). Web start studying chapter 5:
Learn Vocabulary, Terms And More With Flashcards, Games And Other Study Tools.
Web 32 terms · n= → number of sub levels, n^2 → number of orbitals, 2n^2 → number of electrons in each en…, energy level is →. Both are orbitals that can contain two electrons. The height of a wave from the origin to a crest,or from the origin to a trough. Atoms are made of extremely tiny particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons.