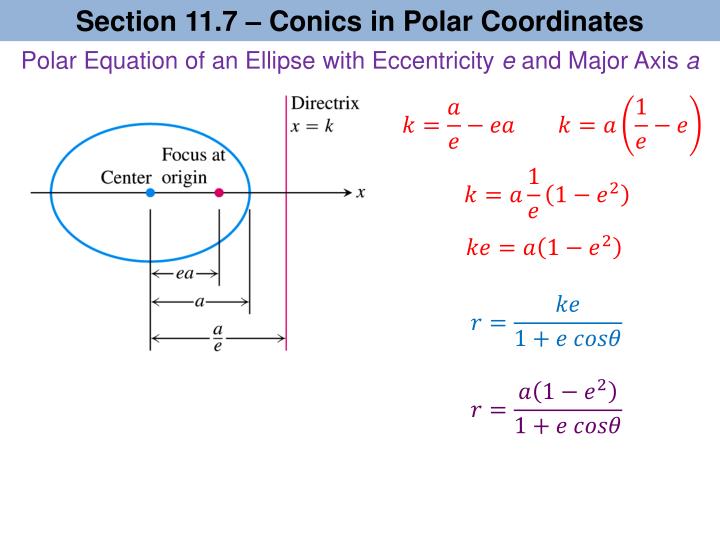
Ellipse Polar Form
Ellipse Polar Form - R d − r cos ϕ = e r d − r cos ϕ = e. Web polar equation to the ellipse; For the description of an elliptic orbit, it is convenient to express the orbital position in polar coordinates, using the angle θ: Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches the periapsis and decrease as it approaches the apoapsis. Web the polar form of a conic to create a general equation for a conic section using the definition above, we will use polar coordinates. Web formula for finding r of an ellipse in polar form. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in. Web ellipses in polar form michael cheverie 77 subscribers share save 63 views 3 years ago playing with the equation of an ellipse in polar form on desmos, the online graphing calculator, by. Figure 11.5 a a b b figure 11.6 a a b b if a < Web in an elliptical orbit, the periapsis is the point at which the two objects are closest, and the apoapsis is the point at which they are farthest apart.
Web in mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. (it’s easy to find expressions for ellipses where the focus is at the origin.) I couldn’t easily find such an equation, so i derived it and am posting it here. Represent q(x, y) in polar coordinates so (x, y) = (rcos(θ), rsin(θ)). Web formula for finding r of an ellipse in polar form. Web the equation of a horizontal ellipse in standard form is \(\dfrac{(x−h)^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{(y−k)^2}{b^2}=1\) where the center has coordinates \((h,k)\), the major axis has length 2a, the minor axis has length 2b, and the coordinates of the foci are \((h±c,k)\), where \(c^2=a^2−b^2\). Start with the formula for eccentricity. I have the equation of an ellipse given in cartesian coordinates as ( x 0.6)2 +(y 3)2 = 1 ( x 0.6) 2 + ( y 3) 2 = 1. Then substitute x = r(θ) cos θ x = r ( θ) cos θ and y = r(θ) sin θ y = r ( θ) sin θ and solve for r(θ) r ( θ). For the description of an elliptic orbit, it is convenient to express the orbital position in polar coordinates, using the angle θ:
Web it's easiest to start with the equation for the ellipse in rectangular coordinates: This form makes it convenient to determine the aphelion and perihelion of. I have the equation of an ellipse given in cartesian coordinates as ( x 0.6)2 +(y 3)2 = 1 ( x 0.6) 2 + ( y 3) 2 = 1. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in. Web polar equation to the ellipse; Web an ellipse is the set of all points (x, y) in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. The family of ellipses handled in the quoted passage was chosen specifically to have a simple equation in polar coordinates. Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches the periapsis and decrease as it approaches the apoapsis. Web ellipses in polar form michael cheverie 77 subscribers share save 63 views 3 years ago playing with the equation of an ellipse in polar form on desmos, the online graphing calculator, by. Web the equation of an ellipse is in the form of the equation that tells us that the directrix is perpendicular to the polar axis and it is in the cartesian equation.
Equation For Ellipse In Polar Coordinates Tessshebaylo
Web polar equation to the ellipse; It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in. Web an ellipse is the set of all points (x, y) in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. Web the ellipse the standard form is (11.2) x2 a2 + y2 b2 =.
Polar description ME 274 Basic Mechanics II
The family of ellipses handled in the quoted passage was chosen specifically to have a simple equation in polar coordinates. An ellipse is defined as the locus of all points in the plane for which the sum of the distance r 1 {r_1} r 1 and r 2 {r_2} r 2 are the two fixed points f 1 {f_1} f.
Equation For Ellipse In Polar Coordinates Tessshebaylo
I need the equation for its arc length in terms of θ θ, where θ = 0 θ = 0 corresponds to the point on the ellipse intersecting the positive x. R d − r cos ϕ = e r d − r cos ϕ = e. Web beginning with a definition of an ellipse as the set of points.
Example of Polar Ellipse YouTube
Web polar equation to the ellipse; It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in. An ellipse is defined as the locus of all points in the plane for which the sum of the distance r 1 {r_1} r 1 and r 2 {r_2} r 2 are the two fixed points f 1 {f_1} f 1 and.
Ellipse (Definition, Equation, Properties, Eccentricity, Formulas)
Web a slice perpendicular to the axis gives the special case of a circle. Pay particular attention how to enter the greek letter theta a. As you may have seen in the diagram under the directrix section, r is not the radius (as ellipses don't have radii). Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches.
Equation Of Ellipse Polar Form Tessshebaylo
As you may have seen in the diagram under the directrix section, r is not the radius (as ellipses don't have radii). I need the equation for its arc length in terms of θ θ, where θ = 0 θ = 0 corresponds to the point on the ellipse intersecting the positive x. Web the polar form of a conic.
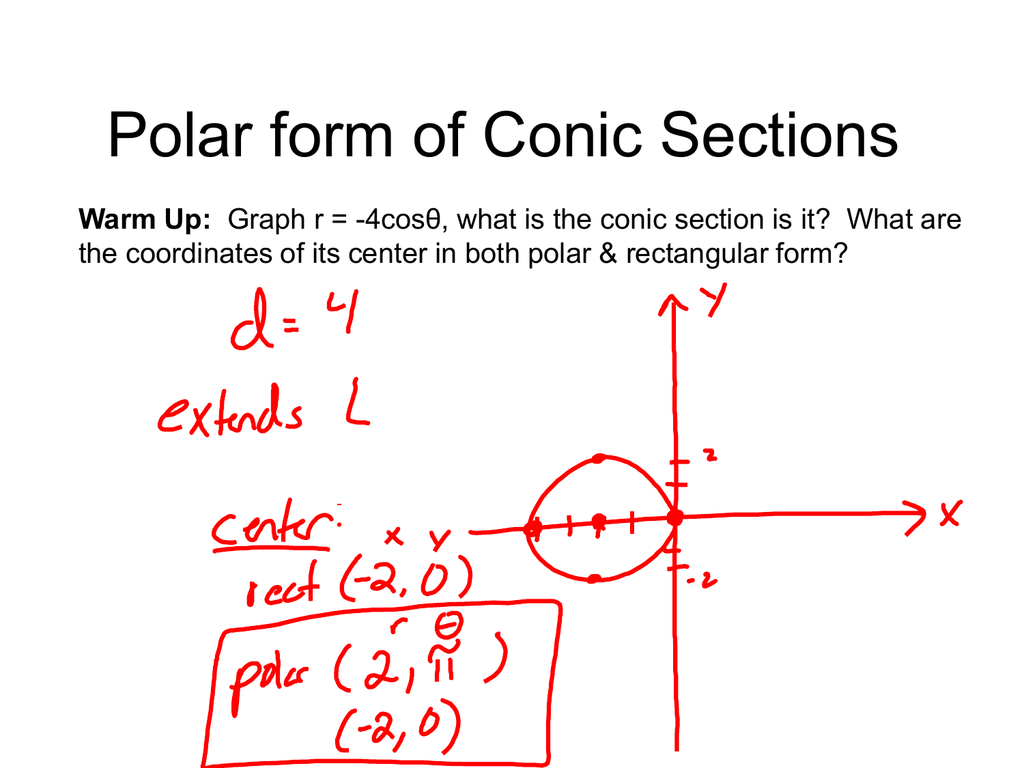
Conics in Polar Coordinates Unified Theorem for Conic Sections YouTube
If the endpoints of a segment are moved along two intersecting lines, a fixed point on the segment (or on the line that prolongs it) describes an arc of an ellipse. Each fixed point is called a focus (plural: I couldn’t easily find such an equation, so i derived it and am posting it here. Web in an elliptical orbit,.
Ellipses in Polar Form YouTube
(it’s easy to find expressions for ellipses where the focus is at the origin.) Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches the periapsis and decrease as it. We easily get the polar equation. As you may have seen in the diagram under the directrix section, r is not the radius (as ellipses don't have.
calculus Deriving polar coordinate form of ellipse. Issue with length
If the endpoints of a segment are moved along two intersecting lines, a fixed point on the segment (or on the line that prolongs it) describes an arc of an ellipse. Web a slice perpendicular to the axis gives the special case of a circle. Web ellipses in polar form michael cheverie 77 subscribers share save 63 views 3 years.
Ellipses in Polar Form Ellipses
Web it's easiest to start with the equation for the ellipse in rectangular coordinates: The polar form of an ellipse, the relation between the semilatus rectum and the angular momentum, and a proof that an ellipse can be drawn using a string looped around the two foci and a pencil that traces out an arc. Web the equation of a.
Place The Thumbtacks In The Cardboard To Form The Foci Of The Ellipse.
Web the equation of an ellipse is in the form of the equation that tells us that the directrix is perpendicular to the polar axis and it is in the cartesian equation. Web a slice perpendicular to the axis gives the special case of a circle. An ellipse can be specified in the wolfram language using circle [ x, y, a , b ]. Web the equation of a horizontal ellipse in standard form is \(\dfrac{(x−h)^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{(y−k)^2}{b^2}=1\) where the center has coordinates \((h,k)\), the major axis has length 2a, the minor axis has length 2b, and the coordinates of the foci are \((h±c,k)\), where \(c^2=a^2−b^2\).
Web In An Elliptical Orbit, The Periapsis Is The Point At Which The Two Objects Are Closest, And The Apoapsis Is The Point At Which They Are Farthest Apart.
Web in an elliptical orbit, the periapsis is the point at which the two objects are closest, and the apoapsis is the point at which they are farthest apart. Web the polar form of a conic to create a general equation for a conic section using the definition above, we will use polar coordinates. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in. Web an ellipse is the set of all points (x, y) in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant.
An Ellipse Is A Figure That Can Be Drawn By Sticking Two Pins In A Sheet Of Paper, Tying A Length Of String To The Pins, Stretching The String Taut With A Pencil, And Drawing The Figure That Results.
Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches the periapsis and decrease as it. Represent q(x, y) in polar coordinates so (x, y) = (rcos(θ), rsin(θ)). The polar form of an ellipse, the relation between the semilatus rectum and the angular momentum, and a proof that an ellipse can be drawn using a string looped around the two foci and a pencil that traces out an arc. R 1 + e cos (1) (1) r d e 1 + e cos.
Web Polar Form For An Ellipse Offset From The Origin.
We can draw an ellipse using a piece of cardboard, two thumbtacks, a pencil, and string. Start with the formula for eccentricity. I have the equation of an ellipse given in cartesian coordinates as ( x 0.6)2 +(y 3)2 = 1 ( x 0.6) 2 + ( y 3) 2 = 1. An ellipse is defined as the locus of all points in the plane for which the sum of the distance r 1 {r_1} r 1 and r 2 {r_2} r 2 are the two fixed points f 1 {f_1} f 1 and f 2 {f_2} f.