Examples Of Row Echelon Form
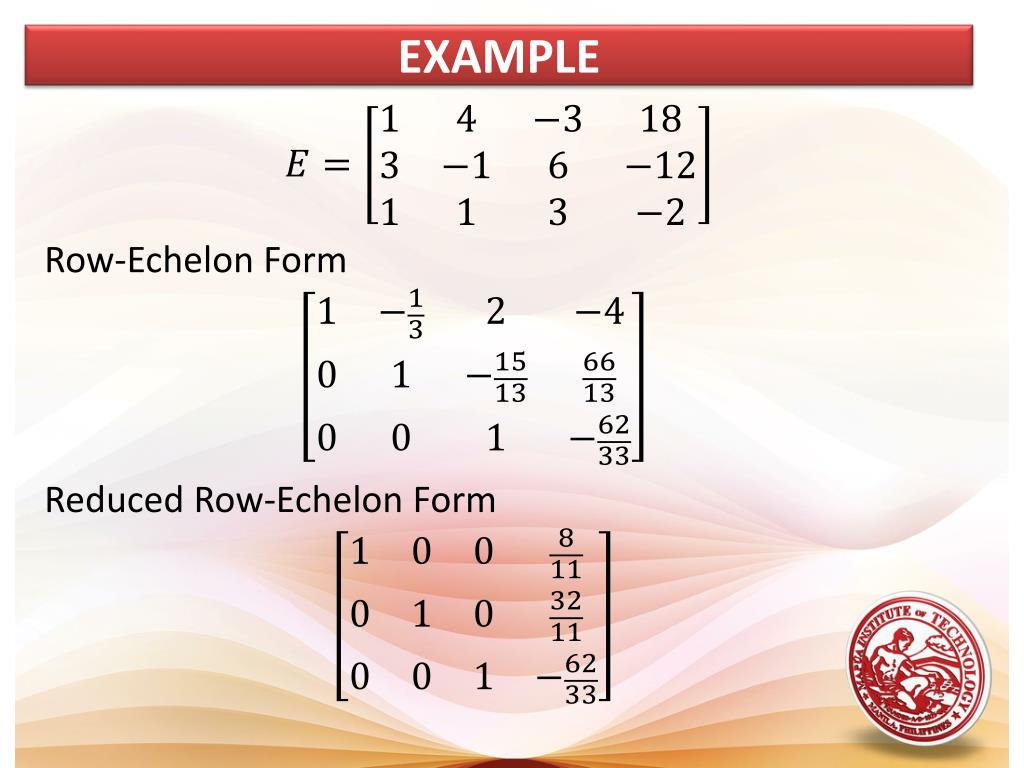
Examples Of Row Echelon Form - There is no more reduced echelon form: The following examples are not in echelon form: Web example the matrix is in row echelon form. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you use. A matrix is in row. Web instead of gaussian elimination and back substitution, a system of equations can be solved by bringing a matrix to reduced row echelon form. Web there is no more than one pivot in any row. Web each of the matrices shown below are examples of matrices in row echelon form. The leading entry ( rst nonzero entry) of each row is to the right of the leading entry. Both the first and the second row have a pivot ( and.
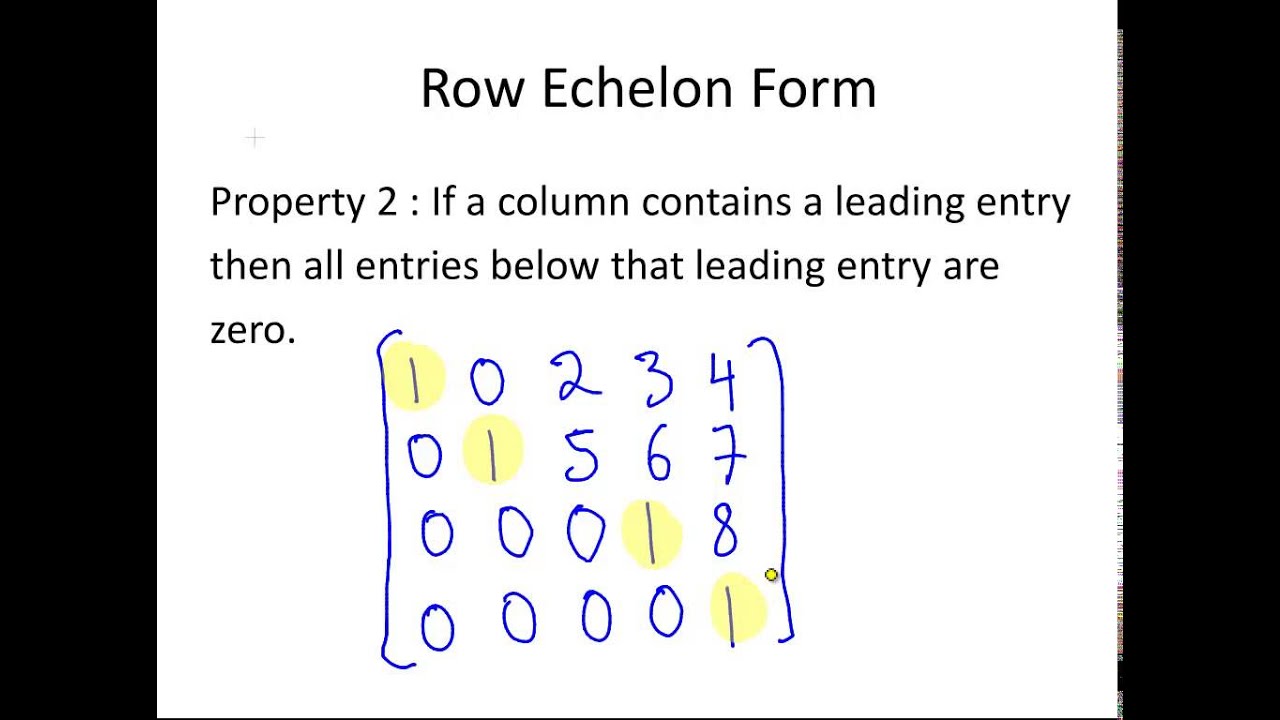
Both the first and the second row have a pivot ( and. All rows with only 0s are on the bottom. The leading entry of each nonzero row after the first occurs to the right of the leading entry of the previous row. Web a matrix is in echelon form if: We can illustrate this by. Web each of the matrices shown below are examples of matrices in row echelon form. Web the following examples are of matrices in echelon form: ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you use. Than one pivot in any column. Web there is no more than one pivot in any row.
Web a matrix is in echelon form if: 1.all nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros. Any matrix can be transformed to reduced row echelon form, using a technique called. Than one pivot in any column. All zero rows are at the bottom of the matrix 2. The leading entry ( rst nonzero entry) of each row is to the right of the leading entry. Web there is no more than one pivot in any row. Web each of the matrices shown below are examples of matrices in row echelon form. There is no more reduced echelon form: We can illustrate this by.
PPT ROWECHELON FORM AND REDUCED ROWECHELON FORM PowerPoint
There is no more reduced echelon form: Example 1 label whether the matrix. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you use. Web since every system can be represented by.
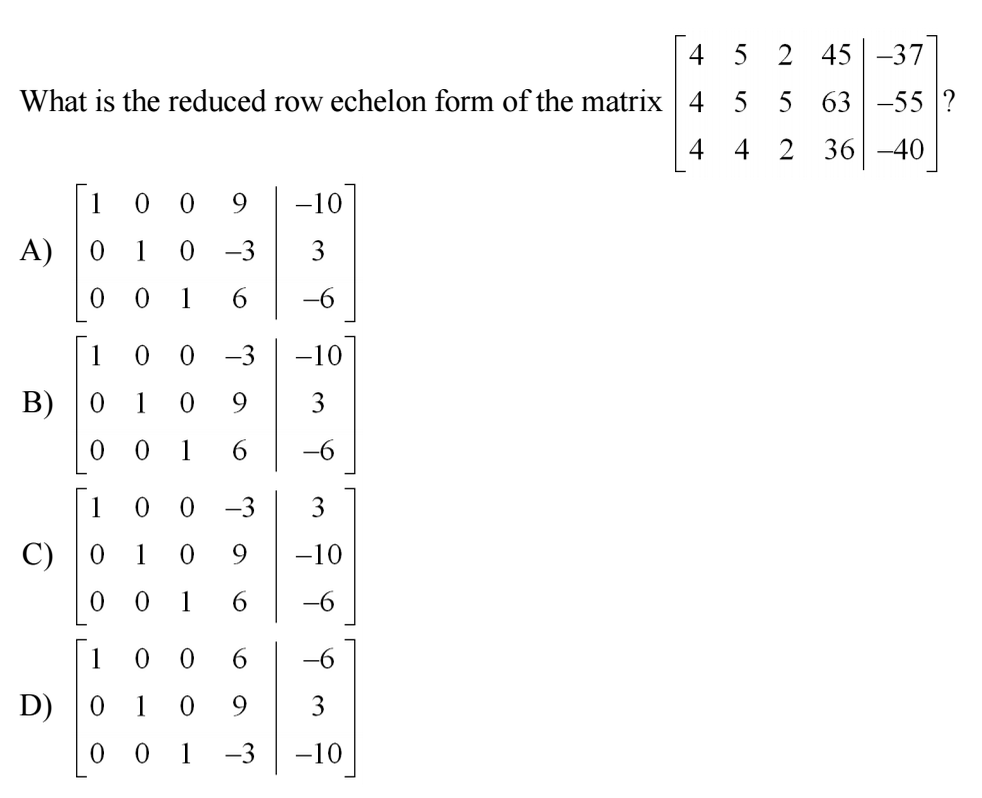
Solved What is the reduced row echelon form of the matrix
The leading entry of each nonzero row after the first occurs to the right of the leading entry of the previous row. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you.
linear algebra Understanding the definition of row echelon form from
There is no more reduced echelon form: Example 1 label whether the matrix. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you use. All rows with only 0s are on the.
Row Echelon (REF) vs. Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) TI 84 Calculator
Web many of the problems you will solve in linear algebra require that a matrix be converted into one of two forms, the row echelon form ( ref) and its stricter variant the. Web since every system can be represented by its augmented matrix, we can carry out the transformation by performing operations on the matrix. Web example the matrix.
Linear Algebra Example Problems Reduced Row Echelon Form YouTube
There is no more reduced echelon form: Example 1 label whether the matrix. A matrix is in row. Web there is no more than one pivot in any row. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same.
Solve a system of using row echelon form an example YouTube
Web since every system can be represented by its augmented matrix, we can carry out the transformation by performing operations on the matrix. Web each of the matrices shown below are examples of matrices in row echelon form. For example, (1 2 3 6 0 1 2 4 0 0 10 30) becomes → {x + 2y + 3z =.
7.3.4 Reduced Row Echelon Form YouTube
All rows with only 0s are on the bottom. Some references present a slightly different description of the row echelon form. For example, (1 2 3 6 0 1 2 4 0 0 10 30) becomes → {x + 2y + 3z = 6 y + 2z. Both the first and the second row have a pivot ( and. Row.
Row Echelon Form of a Matrix YouTube
The leading entry ( rst nonzero entry) of each row is to the right of the leading entry. A matrix is in row. Any matrix can be transformed to reduced row echelon form, using a technique called. The leading entry of each nonzero row after the first occurs to the right of the leading entry of the previous row. Web.
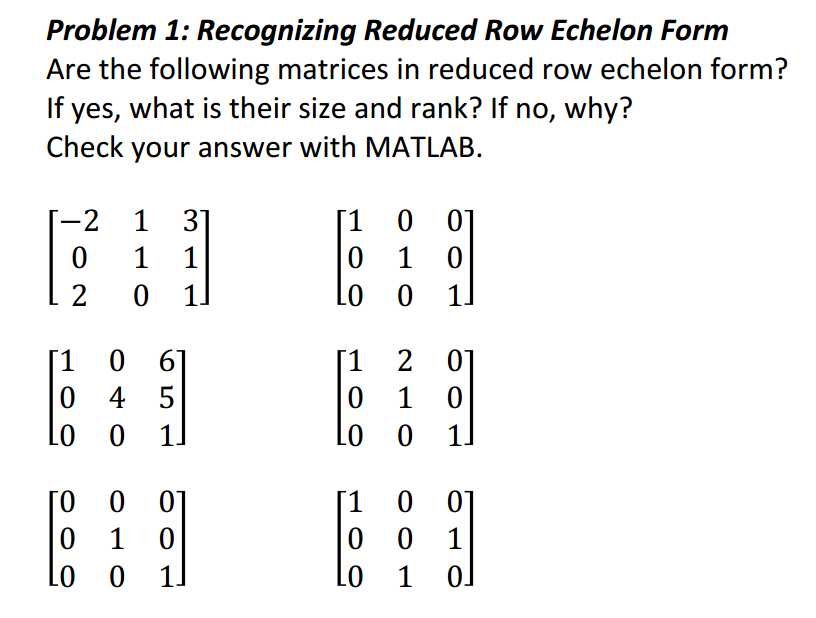
Solved Are The Following Matrices In Reduced Row Echelon
A matrix is in row. ⎡⎣⎢1 0 0 3 1 0 2 3 1 0 2 −4⎤⎦⎥ [ 1 3 2 0 0 1 3 2 0 0 1 − 4] reduced row echelon the same requirements as row echelon, except now you use. Examples (cont.) example (row reduce to echelon form and. Some references present a slightly different description.
Elementary Linear Algebra Echelon Form of a Matrix, Part 1 YouTube
There is no more reduced echelon form: Web since every system can be represented by its augmented matrix, we can carry out the transformation by performing operations on the matrix. Examples (cont.) example (row reduce to echelon form and. Web many of the problems you will solve in linear algebra require that a matrix be converted into one of two.
A Matrix Is In Row.
Both the first and the second row have a pivot ( and. Web each of the matrices shown below are examples of matrices in row echelon form. Web instead of gaussian elimination and back substitution, a system of equations can be solved by bringing a matrix to reduced row echelon form. Examples (cont.) example (row reduce to echelon form and.
Web Example The Matrix Is In Row Echelon Form.
1.all nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros. The following examples are not in echelon form: Web the following examples are of matrices in echelon form: All zero rows are at the bottom of the matrix 2.
Web A Matrix Is In Echelon Form If:
For example, (1 2 3 6 0 1 2 4 0 0 10 30) becomes → {x + 2y + 3z = 6 y + 2z. Row operations for example, let’s take the following system and solve using the elimination method steps. Than one pivot in any column. The leading entry ( rst nonzero entry) of each row is to the right of the leading entry.
The Leading Entry Of Each Nonzero Row After The First Occurs To The Right Of The Leading Entry Of The Previous Row.
All rows with only 0s are on the bottom. Web there is no more than one pivot in any row. We can illustrate this by. Example 1 label whether the matrix.