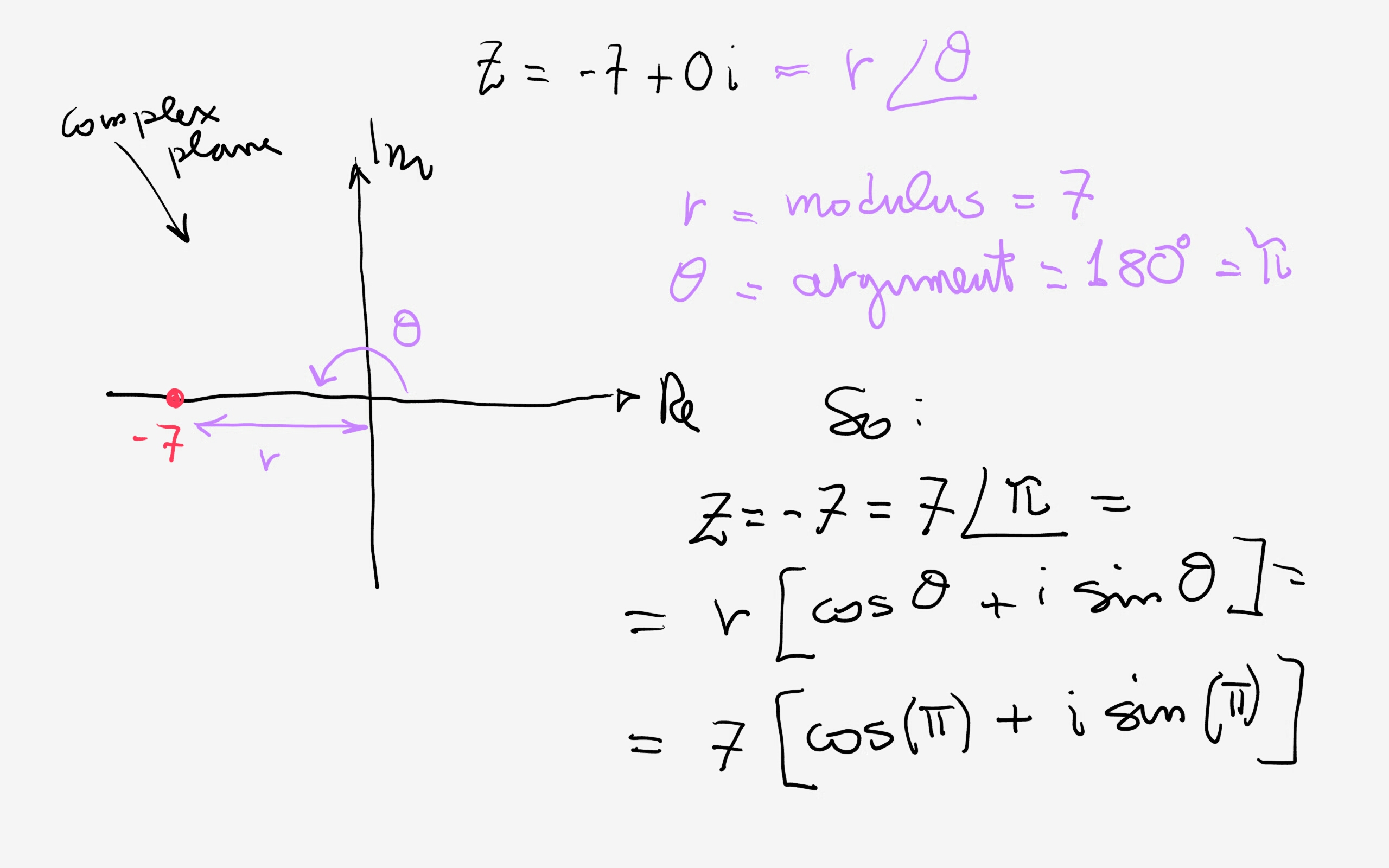Trigonometric Form Of A Vector
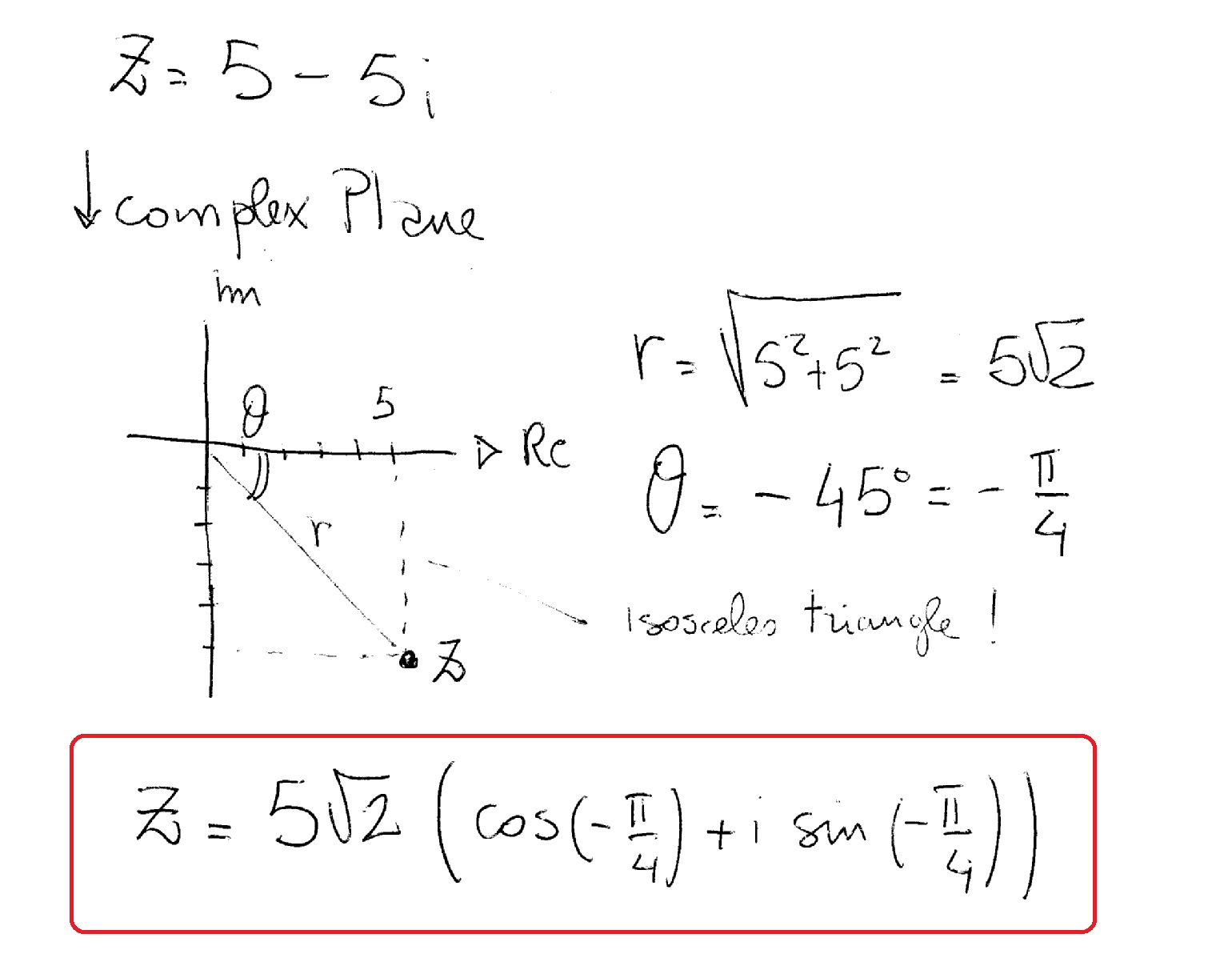
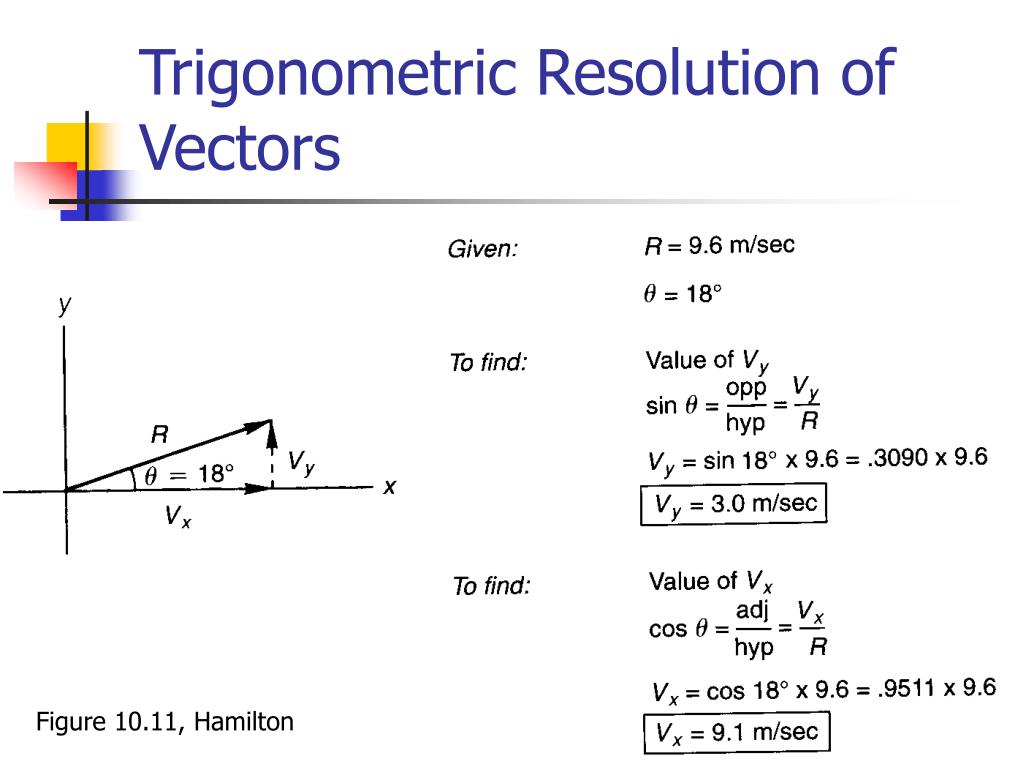
Trigonometric Form Of A Vector - The angle θ is called the argument of the argument of the complex number z and the real number r is the modulus or norm of z. Web z = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)). This is much more clear considering the distance vector that the magnitude of the vector is in fact the length of the vector. Right triangles & trigonometry the reciprocal trigonometric ratios: $$v_x = \lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert \cos θ$$ $$v_y = \lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert \sin θ$$ $$\lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert = \sqrt{v_x^2 + v_y^2}$$ $$\tan θ = \frac{v_y}{v_x}$$ This is the trigonometric form of a complex number where |z| | z | is the modulus and θ θ is the angle created on the complex plane. Component form in component form, we treat the vector as a point on the coordinate plane, or as a directed line segment on the plane. Web when finding the magnitude of the vector, you use either the pythagorean theorem by forming a right triangle with the vector in question or you can use the distance formula. Plug the solutions into the definition of. 2.1.6 give two examples of vector quantities.
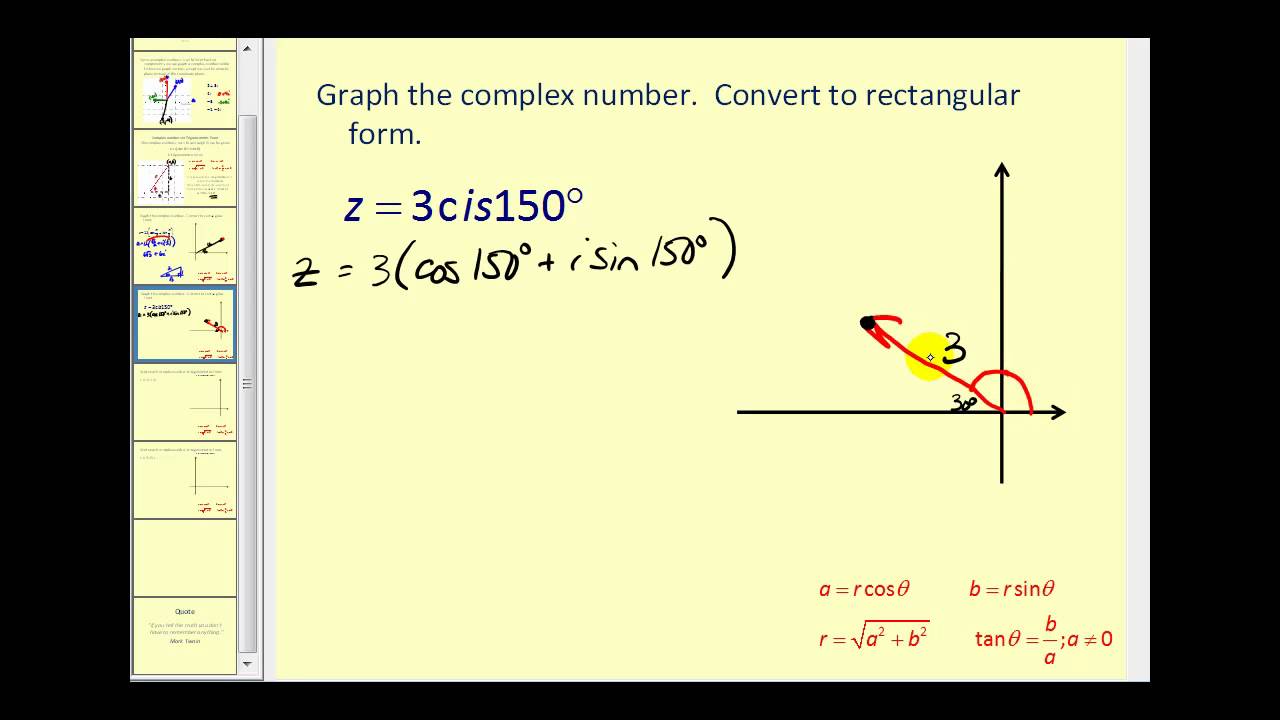
We will also be using these vectors in our example later. The direction of a vector is only fixed when that vector is viewed in the coordinate plane. The length of the arrow (relative to some kind of reference or scale) represents the relative magnitude of the vector while the arrow head gives. Web a vector is defined as a quantity with both magnitude and direction. This is the trigonometric form of a complex number where |z| | z | is the modulus and θ θ is the angle created on the complex plane. Web a vector [math processing error] can be represented as a pointed arrow drawn in space: Component form in component form, we treat the vector as a point on the coordinate plane, or as a directed line segment on the plane. Both component form and standard unit vectors are used. This formula is drawn from the **pythagorean theorem* {math/geometry2/specialtriangles}*. Z = a+ bi = |z|(cos(θ)+isin(θ)) z = a + b i = | z | ( cos ( θ) + i sin ( θ))
The direction of a vector is only fixed when that vector is viewed in the coordinate plane. Web the vector and its components form a right triangle. We will also be using these vectors in our example later. In the above figure, the components can be quickly read. Web what lives trigonometry form? To find \(\overrightarrow{u + v}\), we first draw the vector \(\vec{u}\), and from the terminal end of \(\vec{u}\), we drawn the vector \(\vec{v}\). Plug the solutions into the definition of. 2.1.6 give two examples of vector quantities. This is much more clear considering the distance vector that the magnitude of the vector is in fact the length of the vector. When we write z in the form given in equation 5.2.1 :, we say that z is written in trigonometric form (or polar form).
Trigonometric chart Cuemath
−→ oa and −→ ob. Since displacement, velocity, and acceleration are vector quantities, we can analyze the horizontal and vertical components of each using some trigonometry. Summation of trigonometric form clarity and properties; To find \(\overrightarrow{u + v}\), we first draw the vector \(\vec{u}\), and from the terminal end of \(\vec{u}\), we drawn the vector \(\vec{v}\). Web what are the.
18+ trigonometric form of a vector KhailaMillen
Web how to write a component form vector in trigonometric form (using the magnitude and direction angle). Z = a+ bi = |z|(cos(θ)+isin(θ)) z = a + b i = | z | ( cos ( θ) + i sin ( θ)) 2.1.6 give two examples of vector quantities. Given the coordinates of a vector (x, y), its magnitude is..
Trigonometric Form To Polar Form
Web when finding the magnitude of the vector, you use either the pythagorean theorem by forming a right triangle with the vector in question or you can use the distance formula. How to write a component. In the above figure, the components can be quickly read. Web a vector [math processing error] can be represented as a pointed arrow drawn.
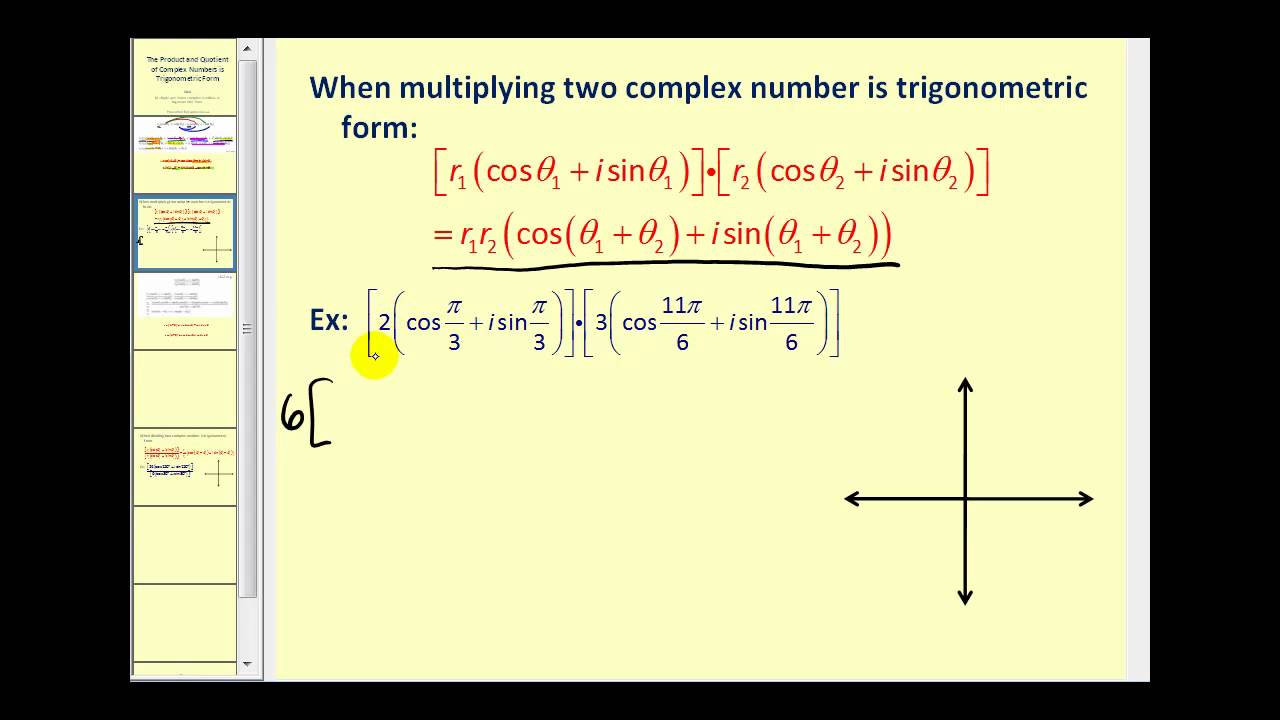
The Product and Quotient of Complex Numbers in Trigonometric Form YouTube
ˆu = < 2,5 >. Two vectors are shown below: This is the trigonometric form of a complex number where |z| | z | is the modulus and θ θ is the angle created on the complex plane. Or if you had a vector of magnitude one, it would be cosine of that angle, would be the x component, for.
Vector Components Trigonometry Formula Sheet Math words, Math quotes
In the above figure, the components can be quickly read. Web solving for an angle in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios: −→ oa and −→ ob. Summation of trigonometric form clarity and properties; Since displacement, velocity, and acceleration are vector quantities, we can analyze the horizontal and vertical components of each using some trigonometry.
Trigonometric Form To Standard Form
Web what lives trigonometry form? $$v_x = \lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert \cos θ$$ $$v_y = \lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert \sin θ$$ $$\lvert \overset{\rightharpoonup}{v} \rvert = \sqrt{v_x^2 + v_y^2}$$ $$\tan θ = \frac{v_y}{v_x}$$ Web to find the direction of a vector from its components, we take the inverse tangent of the ratio of the components: Plug the solutions into the definition of. Cosine.
Vectors in Trigonmetric Form YouTube
Add in the triangle legs. Or if you had a vector of magnitude one, it would be cosine of that angle, would be the x component, for the, if we had a unit vector there in that direction. Component form in component form, we treat the vector as a point on the coordinate plane, or as a directed line segment.
Trigonometric Form To Standard Form
Want to learn more about vector component form? Z = a+ bi = |z|(cos(θ)+isin(θ)) z = a + b i = | z | ( cos ( θ) + i sin ( θ)) Or if you had a vector of magnitude one, it would be cosine of that angle, would be the x component, for the, if we had a.
PPT Introduction to Biomechanics and Vector Resolution PowerPoint
This is much more clear considering the distance vector that the magnitude of the vector is in fact the length of the vector. Since displacement, velocity, and acceleration are vector quantities, we can analyze the horizontal and vertical components of each using some trigonometry. The angle θ is called the argument of the argument of the complex number z and.
Trig Form of a Vector YouTube
Web how to write a component form vector in trigonometric form (using the magnitude and direction angle). 2.1.3 express a vector in component form.; Web the vector and its components form a right triangle. This formula is drawn from the **pythagorean theorem* {math/geometry2/specialtriangles}*. Web what are the different vector forms?
The Trigonometric Ratios Give The Relation Between Magnitude Of The Vector And The Components Of The Vector.
Web the length of a vector is formally called its magnitude. We will also be using these vectors in our example later. When we write z in the form given in equation 5.2.1 :, we say that z is written in trigonometric form (or polar form). Plug the solutions into the definition of.
Add In The Triangle Legs.
Magnitude & direction form of vectors. Right triangles & trigonometry sine and cosine of complementary angles: Web the vector and its components form a right angled triangle as shown below. The length of the arrow (relative to some kind of reference or scale) represents the relative magnitude of the vector while the arrow head gives.
How To Write A Component.
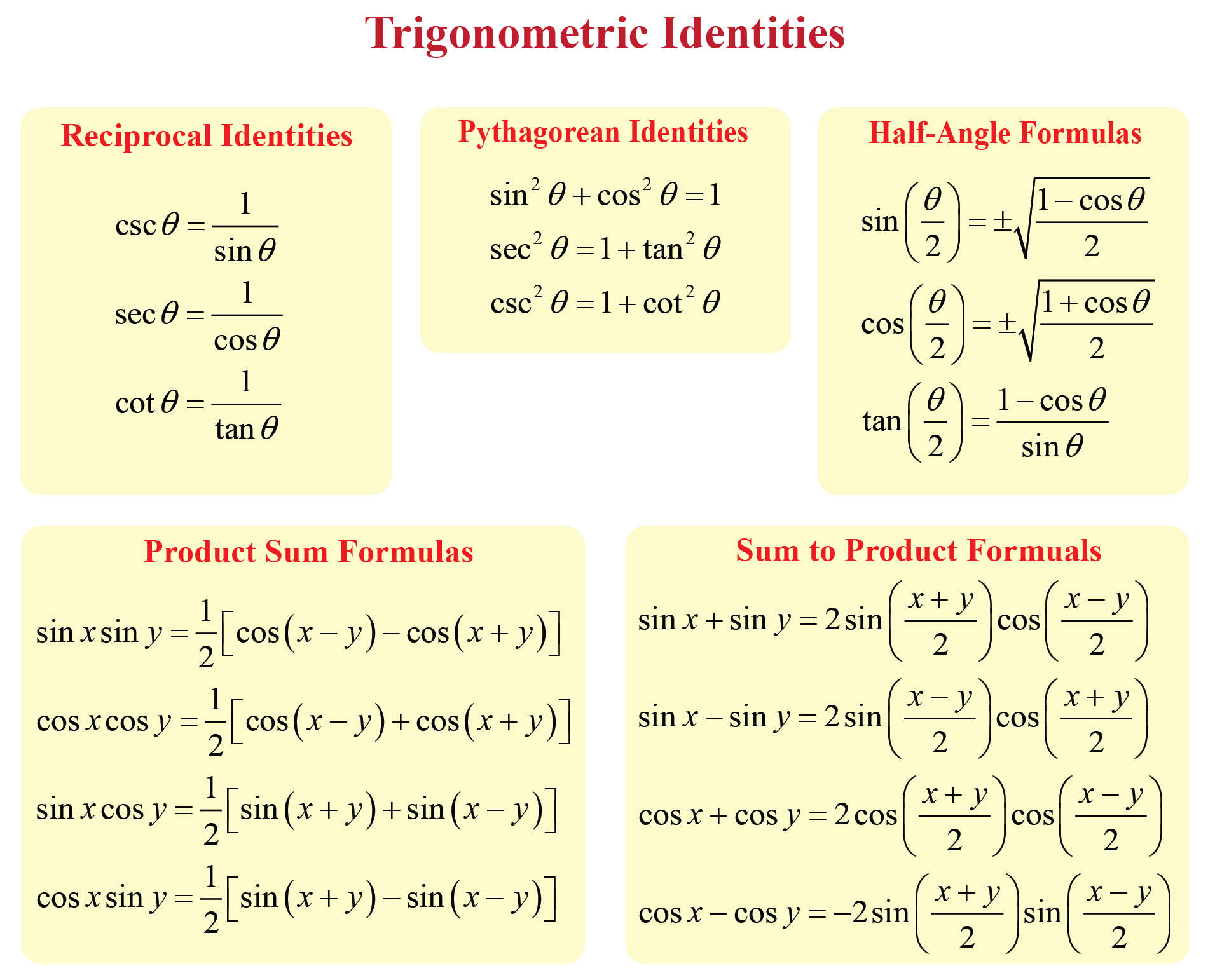
And then sine would be the y component. Web in trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. ˆu = < 2,5 >. To find \(\overrightarrow{u + v}\), we first draw the vector \(\vec{u}\), and from the terminal end of \(\vec{u}\), we drawn the vector \(\vec{v}\).
Z = A+ Bi = |Z|(Cos(Θ)+Isin(Θ)) Z = A + B I = | Z | ( Cos ( Θ) + I Sin ( Θ))
2.1.4 explain the formula for the magnitude of a vector.; Web draw the vector. Course 23k views graphing vectors vectors can be represented graphically using an arrow. Web a vector [math processing error] can be represented as a pointed arrow drawn in space: